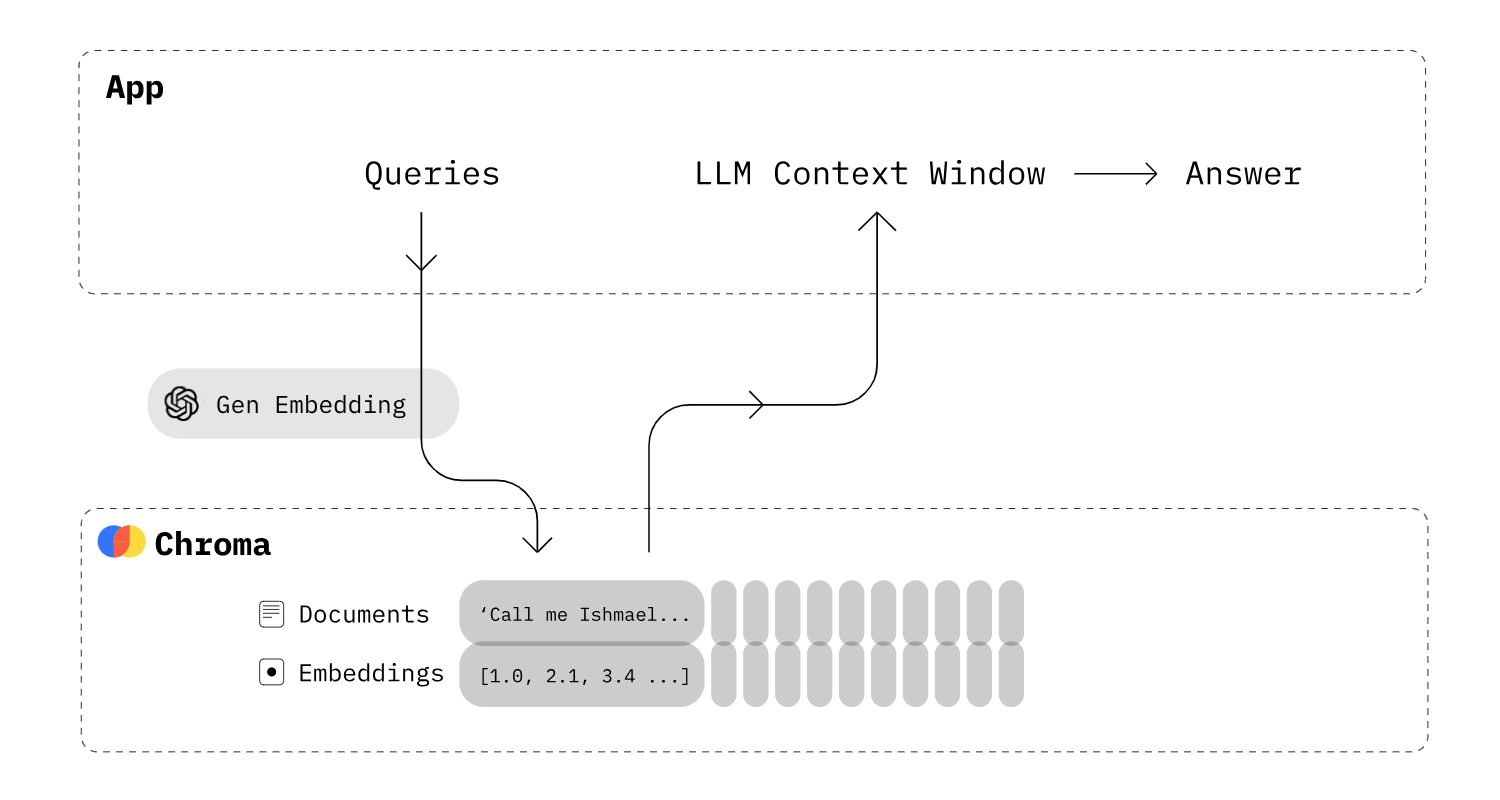
ChatGPT is more than just the GPT model. Similarly, the AI task Question Answering is also more than invoking just one model. This post describes a simple flow that leverages vector search via Chroma and the LangChain library to run the AI pipeline.
As explained in my post Generative AI for Question Answering Scenarios answer generation is typically a process with several steps. First documents are searched, for example via classic MB25/keyword searches or via neural information seek. The top search results are passed as context in the prompts of the Large Language Models to generate the answers. This post explains on a high level how such a Retrieval Augmented Generation pipeline can be implemented.
Chroma
Several databases and search engines have recently added vector-based searches, for example Elasticsearch and Postgres. Another lightweight solution is Chroma.
Chroma is the open-source embedding database. Chroma makes it easy to build LLM apps by making knowledge, facts, and skills pluggable for LLMs.
With the Chroma library documents can be stored as embeddings in the databases. Chroma can convert text to embeddings either automatically or other embedding models can be utilized. My post Searching Documents related to Questions via Embeddings covers the model which currently leads the Hugging Face leaderboard.
LangChain
LangChain is a nice utility library to chain operations together.
LangChain’s flexible abstractions and extensive toolkit enables developers to harness the power of LLMs. […] Tinkerers, startups, research labs, and global corporations rely on LangChain to build for any use-case at any scale.
The LangChain Question Answering documentation describes how to set up the database, how to split documents and how to create embeddings as well as how to retrieve documents/passages from the database and how to pass them into prompts.
Example
Let’s look at an example where documents are retrieved from the vector database Chroma and passed into prompts for the answer generation of large language models.
Import dependencies and load the embeddings and the answer generation models:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
from langchain.embeddings import HuggingFaceBgeEmbeddings
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
embedding = HuggingFaceBgeEmbeddings(
model_name="BAAI/bge-base-en",
model_kwargs={'device': 'cuda'},
encode_kwargs={'normalize_embeddings': True}
)
llm = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("tiiuae/falcon-40b-instruct", trust_remote_code=True)
Load documents and create the vector database:
1
2
3
4
5
documents = ["doc1", "doc2"]
vectordb = Chroma.from_documents(
documents=documents,
embedding=embedding,
persist_directory='db')
Query database and run answer generation via LangChain RetrievalQA:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=llm,
chain_type="stuff",
retriever=vectordb.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 5}),
return_source_documents=True)
query = "When did IBM acquire Red Hat?"
qa_chain.run(query)
Query database and run answer generation via LangChain RetrievalQA and a custom prompt:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
prompt_template = "Use the following pieces of context to answer the question at the end.
If you do not know the answer, please think rationally and answer from your own knowledge base.
{context}
Question: {question}
"
PROMPT = PromptTemplate(
template=prompt_template, input_variables=["context", "question"]
)
chain_type_kwargs = {"prompt": PROMPT}
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=llm,
chain_type="stuff",
retriever=vectordb.as_retriever(),
chain_type_kwargs=chain_type_kwargs)
query = "When did IBM acquire Red Hat?"
qa_chain.run(query)
Next Steps
To learn more, check out the Watsonx.ai documentation and the Watsonx.ai landing page.