Large Language Models can improve search results significantly, since they don’t try to find exact word matches but passages of text that fit best to the questions. This post explains high level information retrieval concepts and IBM’s leading state of the art model, called Dr.Decr.
The power of Large Language Models in the context of search is well described via these examples:
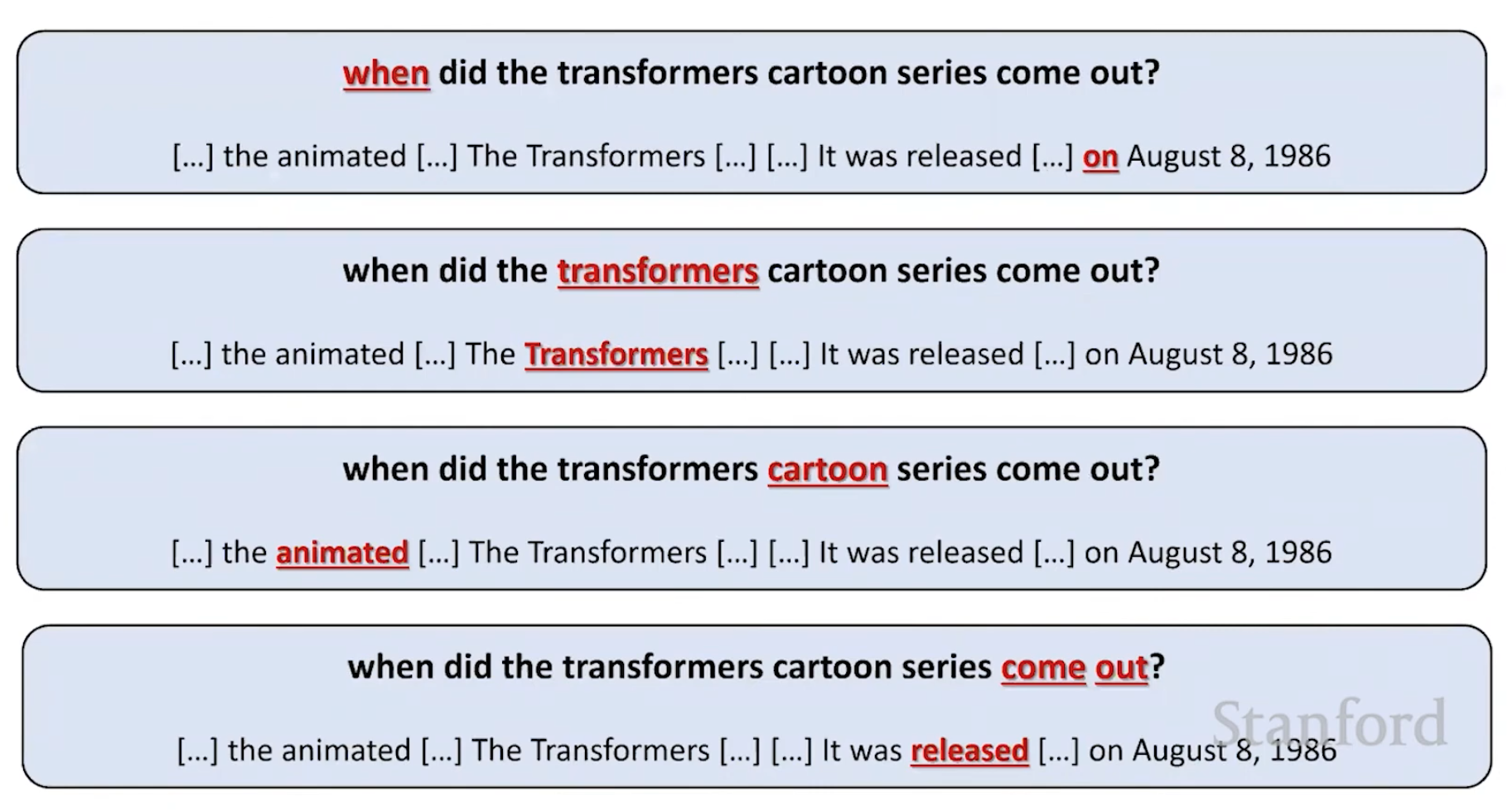
Large Language Models are huge neural networks where neurons are clustered that belong together. For example, words like ‘when’ and ‘on’ in the first sample above have a close relationship in the multi-dimensional network. Rather than trying to find exact word matches, close neighbors are searched.
ColBERT
To leverage these capabilities the first Large Language Models like BERT were used to improve search results. This increased the quality of classic search results but didn’t scale since too many computations had to be done.
Sometimes neural information retrieval models are referred to as ‘Re-Rankers’. Rather than running the model on all documents, another step is prepended that filters documents first, for example via classic full text search. Only the filtered and much smaller set of results is passed to the Large Language Models to increase speed and save compute resources.
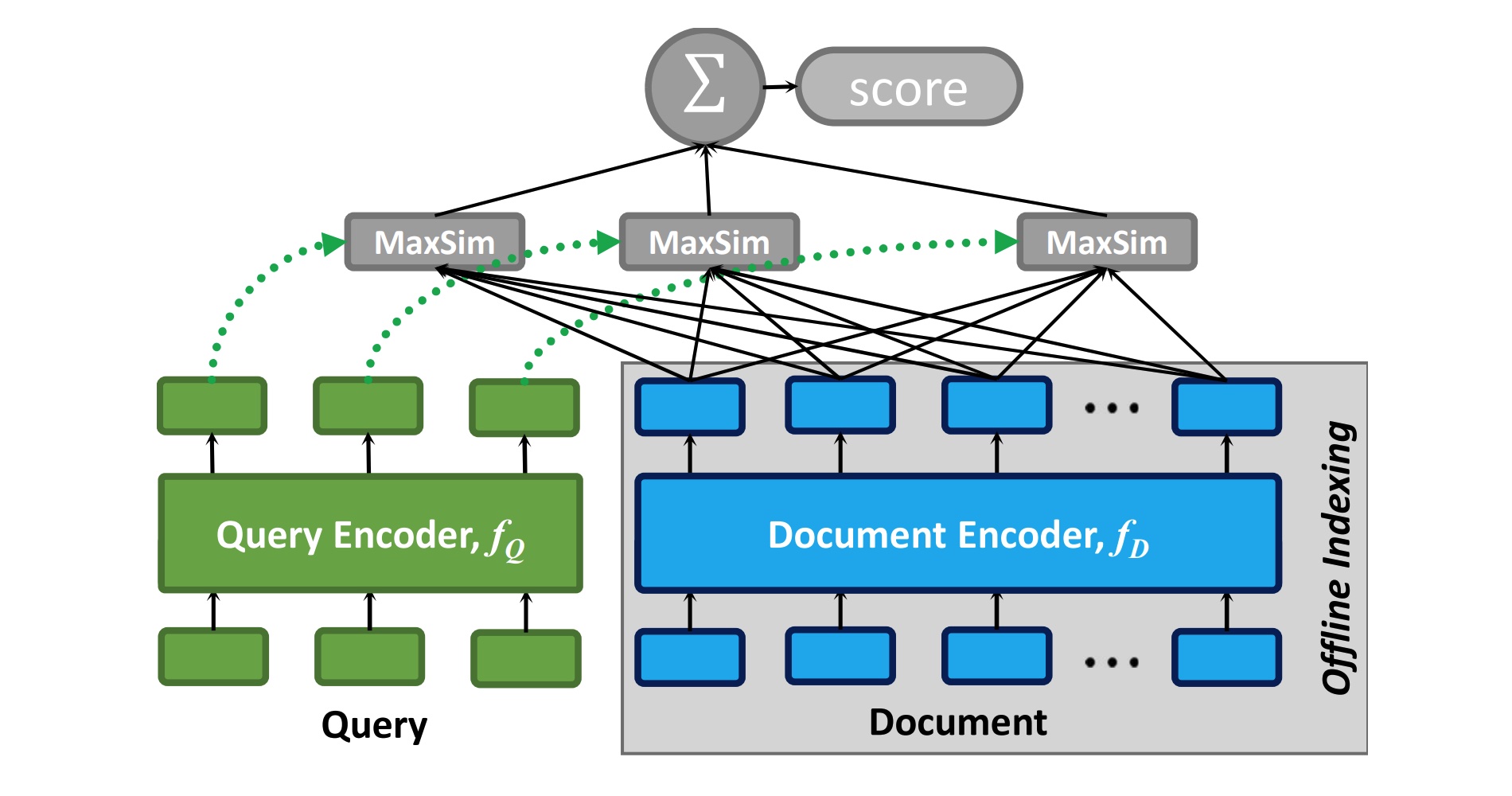
The next generation of information retrieval specialized models is called ColBERT, see the diagram at the top of this post and ColBERT (v2) on GitHub:
As Figure 1 illustrates, ColBERT relies on fine-grained contextual late interaction: it encodes each passage into a matrix of token-level embeddings (shown above in blue). Then at search time, it embeds every query into another matrix (shown in green) and efficiently finds passages that contextually match the query using scalable vector-similarity (MaxSim) operators.
ColBERT models can be used as re-rankers, but since they are very fast they can also be used without previous full text searches in certain scenarios.
Dr.Decr
There are different implementations of the ColBERT concept and there is a lot of progress in this space. The Cross-lingual Open-Retrieval Question Answering leadership board lists the current state of the art models.
IBM has built a model Dr.Decr which stands for Dense Retrieval with Distillation-Enhanced Cross-Lingual Representation. From my experience I can say that this this model works extremely well to find relevant information.
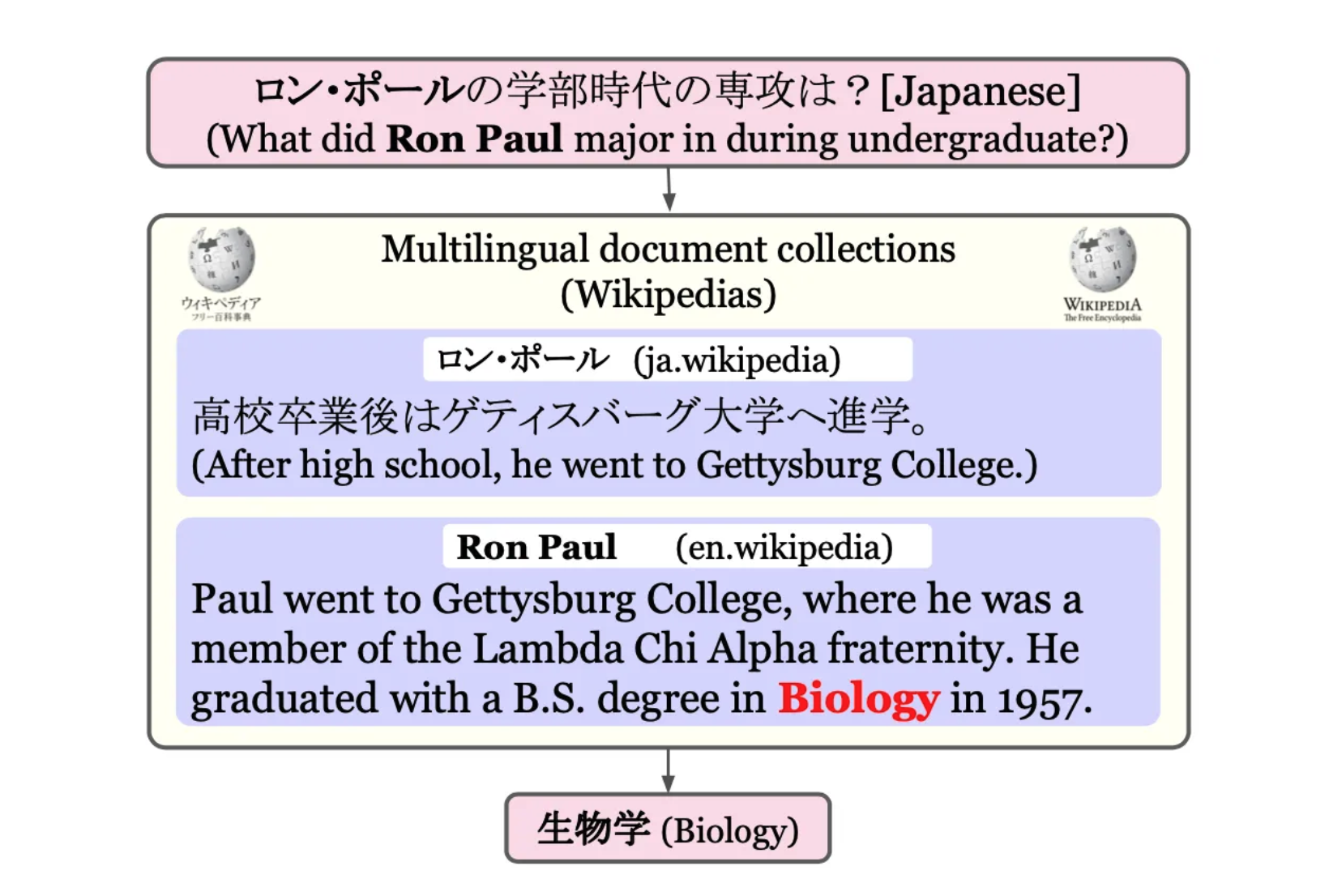
One of the novelties of this model is that it is multi lingual. The next image shows that an answer to a Chinese question can be found in an English corpus of data without having to do the extra translation step.
Sample REST API Invocation
Here is a simple sample how Dr.Decr can be invoked and what data it returns.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
curl -X 'POST' \
'http://<my-host-ip>:50052/RerankRequest' \
-H 'accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"reranker": {
"reranker_id": "ColBERTReranker",
"parameters": [
{
"parameter_id": "model",
"value": "primeqa/store/checkpoints/drdecr/colbert.dnn.batch_72000.model"
}
]
},
"queries": [
"How to I position an index?"
],
"hitsperquery": [
[
{
"document": {
"text": "Indexes on partitioned tables The following types of indexes apply to only partitioned tables: partitioned indexes, partitioning indexes (PIs), data-partitioned secondary indexes (DPSIs) ...",
"document_id": "0",
"title": "Indexes"
},
"score": 1.4
},
{
"document": {
"text": "Bind options for remote access Binding a package to run at a remote location is like binding a package to run at your local Db2 subsystem. Binding a plan to run the package is ...",
"document_id": "1",
"title": "Remote access"
},
"score": 1.4
}
]
]
}'
[
[
{
"document": {
"text": "Indexes on partitioned tables The following types of indexes apply to only partitioned tables: partitioned indexes, partitioning indexes (PIs), data-partitioned secondary indexes (DPSIs) ...",
"document_id": "0",
"title": "Indexes"
},
"score": 22.14895248413086
},
{
"document": {
"text": "Bind options for remote access Binding a package to run at a remote location is like binding a package to run at your local Db2 subsystem. Binding a plan to run the package is ...",
"document_id": "1",
"title": "Remote access"
},
"score": 13.350204467773438
}
]
]
Setup
To try Dr.Decr, you can set it up in PrimeQA. Follow the setup instructions and invoke the following commands.
As part of these instructions you need to download the model from Hugging Face.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
ssh root@<my-host-ip>
git clone https://github.com/primeqa/primeqa.git
cd primeqa/
docker build -f Dockerfiles/Dockerfile.cpu -t primeqa:$(cat VERSION) --build-arg image_version:$(cat VERSION) .
cd ~/<my-dir>/create-primeqa-app/primeqa-store/checkpoints/
mkdir drdecr
cd drdecr
wget https://huggingface.co/PrimeQA/DrDecr_XOR-TyDi_whitebox/resolve/main/DrDecr.dnn
cd ~/<my-dir>/create-primeqa-app
docker run --detach --name primeqa-rest -it -p 50052:50052 --mount type=bind,source="$(pwd)"/primeqa-store,target=/store --mount type=bind,source="$(pwd)"/cache/huggingface/,target=/cache/huggingface/ -e STORE_DIR=/store -e mode=rest -e require_ssl=false primeqa:0:14:1
The OpenAPI UI will be available under ‘:50052/docs’.