Large Language Models are extremely powerful, but they can only return data that existed when they were trained and they cannot invoke APIs and business logic. The technique ReAct combines Chain-of-Thought reasoning and invocations of actions.
To work around the challenge of outdated models and to be able to handle non-public data, techniques like Retrieval Augmented Generation are frequently used which pass relevant information as context to the prompts. Reasoning and Acting utilizes a similar approach where relevant content is added to the prompts.
The following documents are great resources to learn ReAct:
- Paper ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models
- Blog Post ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models
- LangChain ReAct
- Understanding ReACT with LangChain
- Colab from video Understanding ReACT with LangChain
Note: ReAct in AI has nothing to do with the web development framework React.
Reasoning
I’ve described the concept reasoning in the post Understanding Chain of Thought Prompting. Essentially, models are supported to generate good responses by explaining them how they can do this. In the simplest case the instruction “Think step by step” is added to prompts. Alternatively, multiple samples are provided via few-shot prompting.
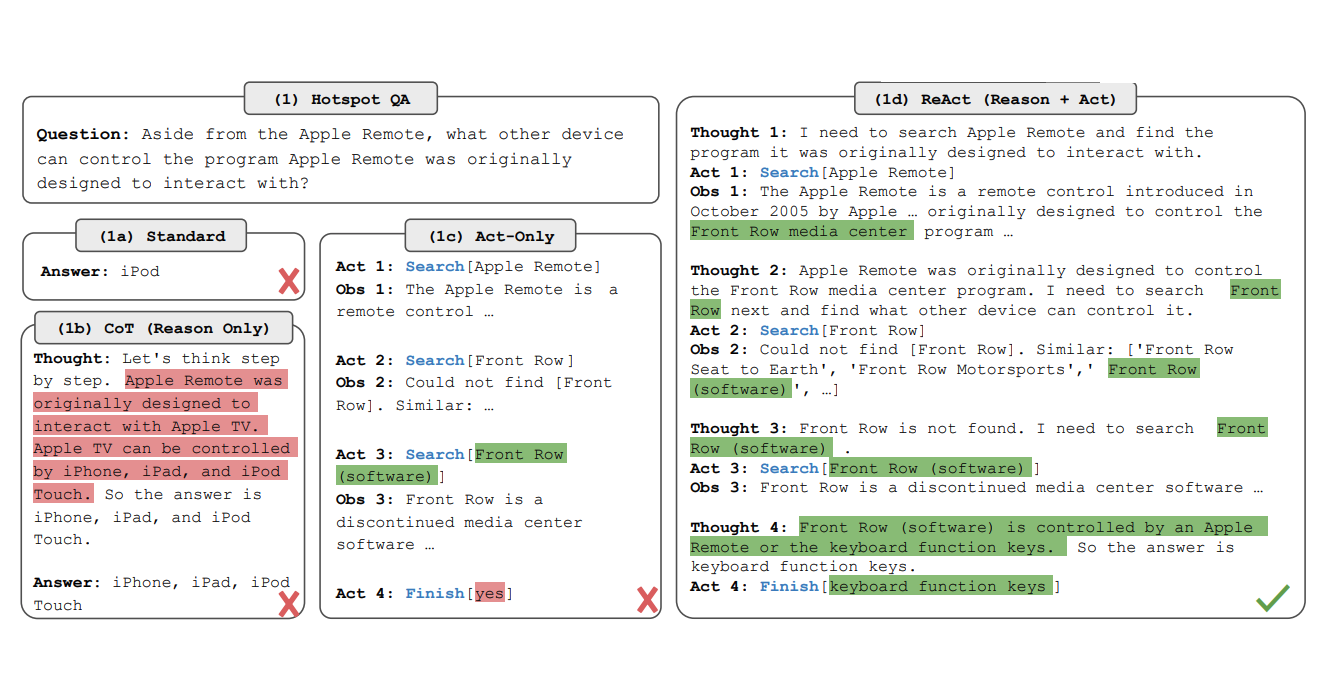
In the example at the top the question “Aside from the Apple Remote, what other device can control the program Apple Remote was originally designed to interact with” needs to be answered. If only the question is put in the prompt, most models fail.
With Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting the answer can be improved, but is still not correct, since most models don’t have this information. The reason why CoT is a good technique is because it tells the model to think about the solution method first, before it generates the response. This is similar to what humans do. If you need to provide an answer to a complex question, you should think about it first.
Acting
In the example above the question is not trivial. I’d have to do some research first too, for example by finding out which program the Apple Remote was originally designed for. The acting part in ReAct can invoke external APIs, logic, databases, etc., for example invoking queries on Wikipedia. So, ReAct is more than one invocation of a LLM. It’s an agent that performs potentially multiple LLM invocations and knows how to orchestrate these invocations.
The example demonstrates how to find out more about the Apple Remote in the first step, in this case the program ‘Front Row media center’ it was originally designed for. Based on this information it invokes additional lookups to find the actual answer. Technically the prompt gets longer with every step to avoid losing context.
To teach models this orchestration logic, different approaches can be followed. One is to fine-tune models with various successful ReAct prompts. Another alternative is to use few-shot learning. Here is an example from the Colab referenced above.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Question: What profession does Nicholas Ray and Elia Kazan have in common?
Thought: I need to search Nicholas Ray and Elia Kazan, find their professions, then find the profession they have in common.
Action: Search[Nicholas Ray]
Observation: Nicholas Ray (born Raymond Nicholas Kienzle Jr., August 7, 1911 - June 16, 1979) was an American film director, screenwriter, and actor best known for the 1955 film Rebel Without a Cause.
Thought: Professions of Nicholas Ray are director, screenwriter, and actor. I need to search Elia Kazan next and find his professions.
Action: Search[Elia Kazan]
Observation: Elia Kazan was an American film and theatre director, producer, screenwriter and actor.
Thought: Professions of Elia Kazan are director, producer, screenwriter, and actor. So profession Nicholas Ray and Elia Kazan have in common is director, screenwriter, and actor.
Action: Finish[director, screenwriter, actor]
LangChain
LangChain has a nice library to implement these types of agents. To initialize agents, they need to know which models and which tools to use.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent
...
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0)
tools = load_tools(["serpapi", "llm-math"], llm=llm)
agent = initialize_agent(tools, llm, agent=AgentType.ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION, verbose=True)
agent.run("Who is Leo DiCaprio's girlfriend? What is her current age raised to the 0.43 power?")
> Entering new AgentExecutor chain...
I need to find out who Leo DiCaprio's girlfriend is and then calculate her age raised to the 0.43 power.
Action: Search
Action Input: "Leo DiCaprio girlfriend"
Observation: Camila Morrone
Thought: I need to find out Camila Morrone's age
Action: Search
Action Input: "Camila Morrone age"
Observation: 25 years
Thought: I need to calculate 25 raised to the 0.43 power
Action: Calculator
Action Input: 25^0.43
Observation: Answer: 3.991298452658078
Thought: I now know the final answer
Final Answer: Camila Morrone is Leo DiCaprio's girlfriend and her current age raised to the 0.43 power is 3.991298452658078.
> Finished chain.
"Camila Morrone is Leo DiCaprio's girlfriend and her current age raised to the 0.43 power is 3.991298452658078."
Next Steps
To learn more, check out the Watsonx.ai documentation and the Watsonx.ai landing page.