With the TechZone Accelerator Toolkit IBM software, open source projects and custom applications can easily be deployed to various clouds. This article provides an overview how to develop your own GitOps modules to deploy resources to Kubernetes via Helm.
Check out my earlier blog that introduces the toolkit: Introducing IBM’s Toolkit to handle Everything as Code. The toolkit leverages Terrafrom and GitOps and is based on best practices from IBM projects with partners and clients. With the toolkit both infrastructure like Kubernetes clusters as well as Kubernetes resources within clusters can be deployed. Infrastructure resources are deployed via Terraform, resources within clusters via Argo CD.
This article explains how Helm can be used in the TechZone Toolkit to deploy resources to Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters with Argo CD. Helm is a popular package manager for Kubernetes. In the context of the toolkit Helm is the preferred option to deploy Kubernetes resources. Alternatively you could deploy Kubernetes resources directly via yaml files. However, the advantage of Helm is that it can easily be configured for different environments via its built-in templating mechanism. Another advantage of Helm in this context is that Terraform variables can easily be mapped to Helm values which is described below.
To understand the following content, I suggest to read these documents that give some background:
- Blog: Deploying Kubernetes Resources via GitOps
- Blog: Understanding TechZone Toolkit GitOps Modules
- Red Hat blog: Continuous Delivery with Helm and Argo CD
- Argo CD documentation: Helm
- Toolkit documentation: Develop an own GitOps module
Let’s look at a concrete example. We developed a TechZone Toolkit GitOps module to deploy Watson NLP. The repo of the module includes the Helm chart. The chart expects values in the following format, for example to define which NLP models and versions you want to deploy.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
componentName: watson-nlp
acceptLicense: false
serviceType: ClusterIP
imagePullSecrets:
- ibm-entitlement-key
registries:
- name: watson
url: cp.icr.io/cp/ai
runtime:
registry: watson
image: watson-nlp-runtime:1.0.15
models:
- registry: watson
image: watson-nlp_syntax_izumo_lang_en_stock:1.0.5
To allow Argo CD to deploy Watson NLP via the Helm, the Helm chart itself as well as the specific values.yaml file need to be put in the GitOps repo.
GitOps modules are just Terraform modules, but follow additional conventions defined by the toolkit to access the automatically provisioned GitOps repo. Input variables of Terraform (GitOps) modules can be defined in variables.tf.
To enable the toolkit to put the chart as well as the values into the Git repo, the following steps are necessary. First the Terraform input variables are converted to Helm values into JSON format in main.tf.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
values_content = {
"componentName" = "embedded"
"acceptLicense" = var.accept_license
"serviceType" = "ClusterIP"
"registries" = var.registries
"imagePullSecrets" = var.imagePullSecrets
"runtime" = {
"registry": var.runtime_registry
"image": var.runtime_image
}
"models" = var.models
}
layer = "services"
...
}
resource null_resource create_yaml {
provisioner "local-exec" {
command = "${path.module}/scripts/create-yaml.sh '${local.name}' '${local.yaml_dir}'"
environment = {
VALUES_CONTENT = yamlencode(local.values_content)
}
}
}
After this the chart and the values are copied into the ‘services’ payload directory via a script.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
#!/usr/bin/env bash
SCRIPT_DIR=$(cd $(dirname "$0"); pwd -P)
MODULE_DIR=$(cd "${SCRIPT_DIR}/.."; pwd -P)
CHART_DIR=$(cd "${MODULE_DIR}/chart/watson-nlp"; pwd -P)
DEST_DIR="$2"
## Add logic here to put the yaml resource content in DEST_DIR
mkdir -p "${DEST_DIR}"
cp -R "${CHART_DIR}/"* "${DEST_DIR}"
if [[ -n "${VALUES_CONTENT}" ]]; then
echo "${VALUES_CONTENT}" > "${DEST_DIR}/values.yaml"
fi
find "${DEST_DIR}" -name "*"
echo "Files in output path"
ls -l "${DEST_DIR}"
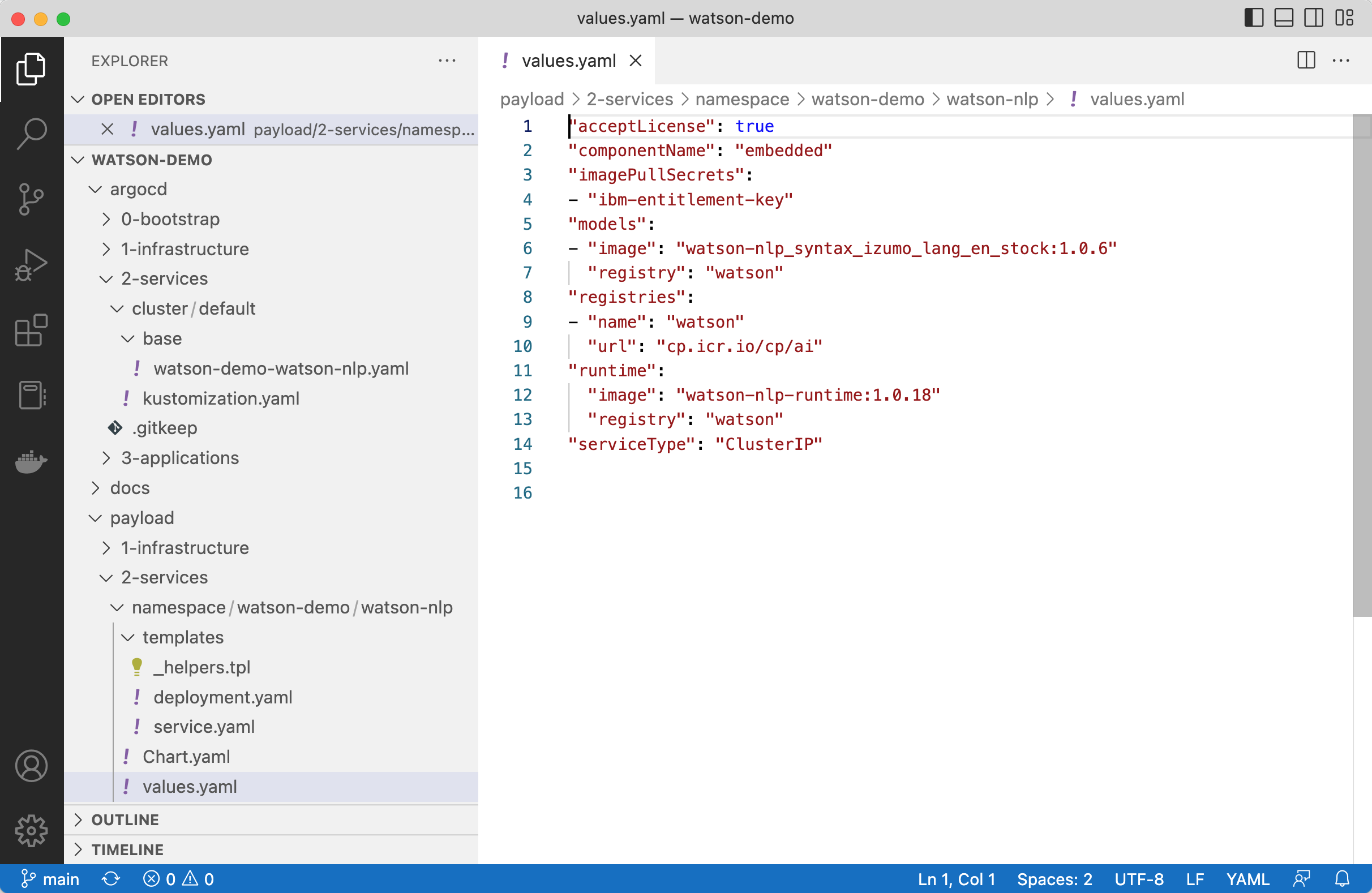
After the toolkit module has been deployed, you’ll find everything in your own GitOps repo as shown in the screenshot above. The values.yaml file does not contain the default chart values, but the input variables of your Terraform module.
To change deployments you can simply change the configuration in the GitOps repo, for example to update to a later version of Watson NLP. Argo CD will be triggered automatically to synchronize the desired state with the actual state.
Combination of Terraform and Argo CD
As you’ve seen, the TechZone Toolkit uses a combination of Terraform and Argo CD. Initially Terraform takes the lead to deploy infrastructure components like VPCs, Kubernetes clusters, Argo CD within clusters and GitOps repos. After this Argo CD is triggered to deploy the initial version of resources as defined in the GitOps repos.
However, after the initial deployments Argo CD takes over the lead. To deploy newer versions of Kubernetes resources, changes can simply be push to Git. When the same Terraform modules are invoked later, for example to deploy more infrastructure components, the toolkit does not modify the already deployed Git repo!
To find out more about these capabilities, check out the following resources: