In March IBM launched the Model Asset Exchange which is a place for developers to find and use open source deep learning models. In this article I describe how developers can use these models in applications and how the applications can be deployed to Kubernetes.
The Model Asset Exchange contains currently 11 models for visual recognition, text generation, style transfer and more. The models are open source and the IP, including for the data, has been vetted.
There are two types of models: Models that can be re-used directly and models with instructions how to train and customize them. I like this concept a lot. I’m a developer and not a data scientist and these models allow me to use AI in my applications without having to write my own neural networks.
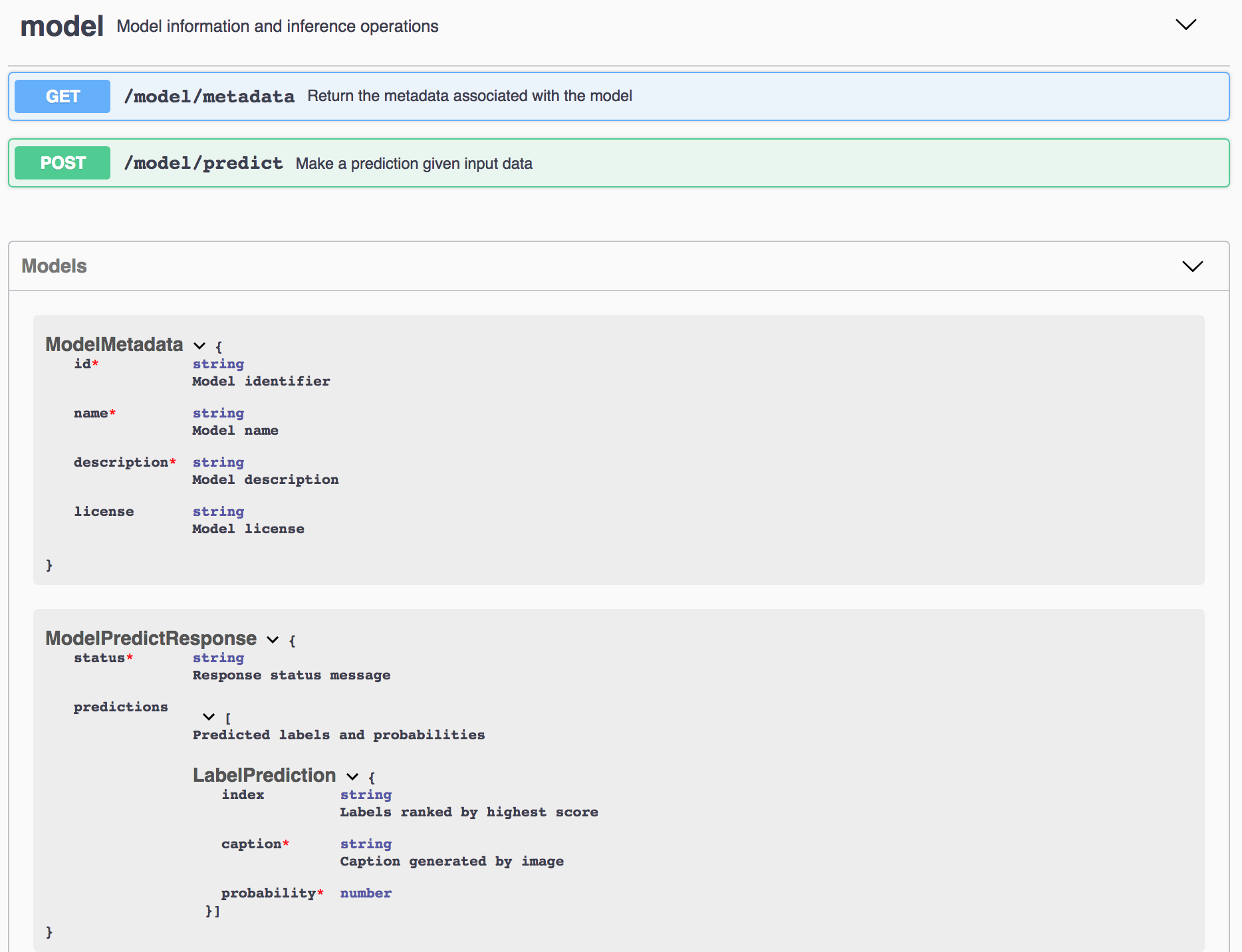
Technically the models are put in Docker images which can be deployed to various environments, for example Kubernetes on the IBM Cloud. The Docker images also abstract which deep learning framework is used. So as a consumer you don’t have to understand the differences between TensorFlow, PyTorch, etc. Instead developers can simply invoke REST APIs to run predictions. Every model comes with a Swagger API definition and an explorer as shown in the screenshot.
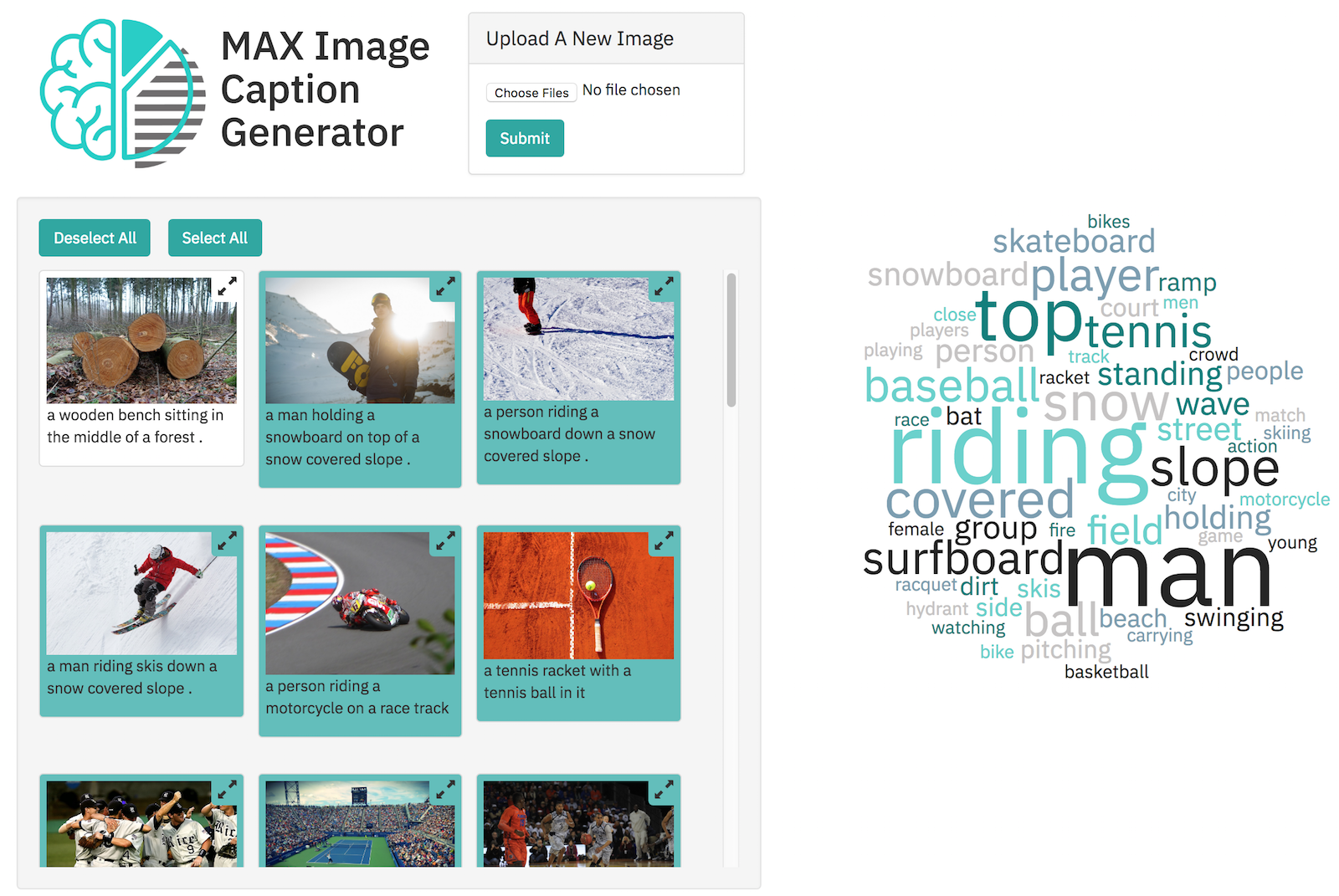
One of the models is the Image Caption Generator. With this model text is generated that describes content on an image. The next screenshot shows a sample web application which uses this model. It also displays a tag cloud. Users can click on a tag and only the images are selected that match this tag.
The Docker images of the models are available on Docker Hub. There are also yaml files for the models to deploy them easily on Kubernetes.
The caption generator web application documents currently how to deploy the model to Kubernetes and how to deploy the web application on the IBM Cloud as Cloud Foundry application. I’ve sent a pull request that also shows how to deploy the web application to Kubernetes.
Check out the yaml file to deploy the web application and the yaml file to deploy the model.
In the model yaml file the service has the name ‘caption-generator-service’:
1
2
3
4
5
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
name: caption-generator-service
name: caption-generator-service
In the web application yaml file this name is passed as argument to the web application:
1
2
3
4
5
6
containers:
- name: caption-generator-web
image: nheidloff/caption-generator-web:latest
command: ["python", "app.py", "--ml-endpoint=http://caption-generator-service:5000"]
ports:
- containerPort: 8088
Want to run this sample yourself?
All you need to do is to get a free IBM Cloud account, create a Kubernetes cluster, get the code from GitHub and run these commands:
1
2
$ kubectl apply -f kube-model.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f kube-web.yaml