Fine-tuning of Large Language Models allows customizations of AI models for specific tasks and data. While Fine-tuning used to require a lot of compute, technologies like InstructLab, QLoRA and lama.cpp have made this process much more efficient. This post describes the evolution of Generative AI customization options with a focus on InstructLab, an innovative open-source project from IBM and Red Hat.
Below are slides of a thought leadership talk that describes InstructLab to a diverse group of people with different technical roles. The first half of the talk covers some background how AI has evolved. The second half focusses on InstructLab which is a framework to fine-tune models easily and efficiently without having to have a deep understanding of data science. Developers can start using InstructLab locally and can leverage cloud-based platforms with GPUs like IBM watsonx.ai for the Fine-tuning with more data and more iterations.
AI Evolution
AI has been around for quite some time, but recently made a huge step forward in the evolution with the introduction of Generative AI, Foundation Models and Transformers.
Classic programming and rule-based systems ran into limitations which could only be solved by machine learning. How would you develop code that differentiates Chihuahuas and muffins?
Rather than writing code, classic Machine Learning leverages sample data. It requires a lot of labeled data to train a model for a specific AI task.
Collecting or creating labeled data is expensive and sometimes not even possible. Generative AI addresses this issue. Instead of training models from scratch for each AI tasks, Large Language Models are pre-trained which can be used for different purposes.
The simple, but genius trick to get enough labeled data, is to use existing data, for example from the internet, cut out certain pieces and leverage these pieces basically as labels. The same trick works for text, audio and images.
The downside of this approach is that you need a big amount of data and pre-training requires a lot of time and GPU resources.
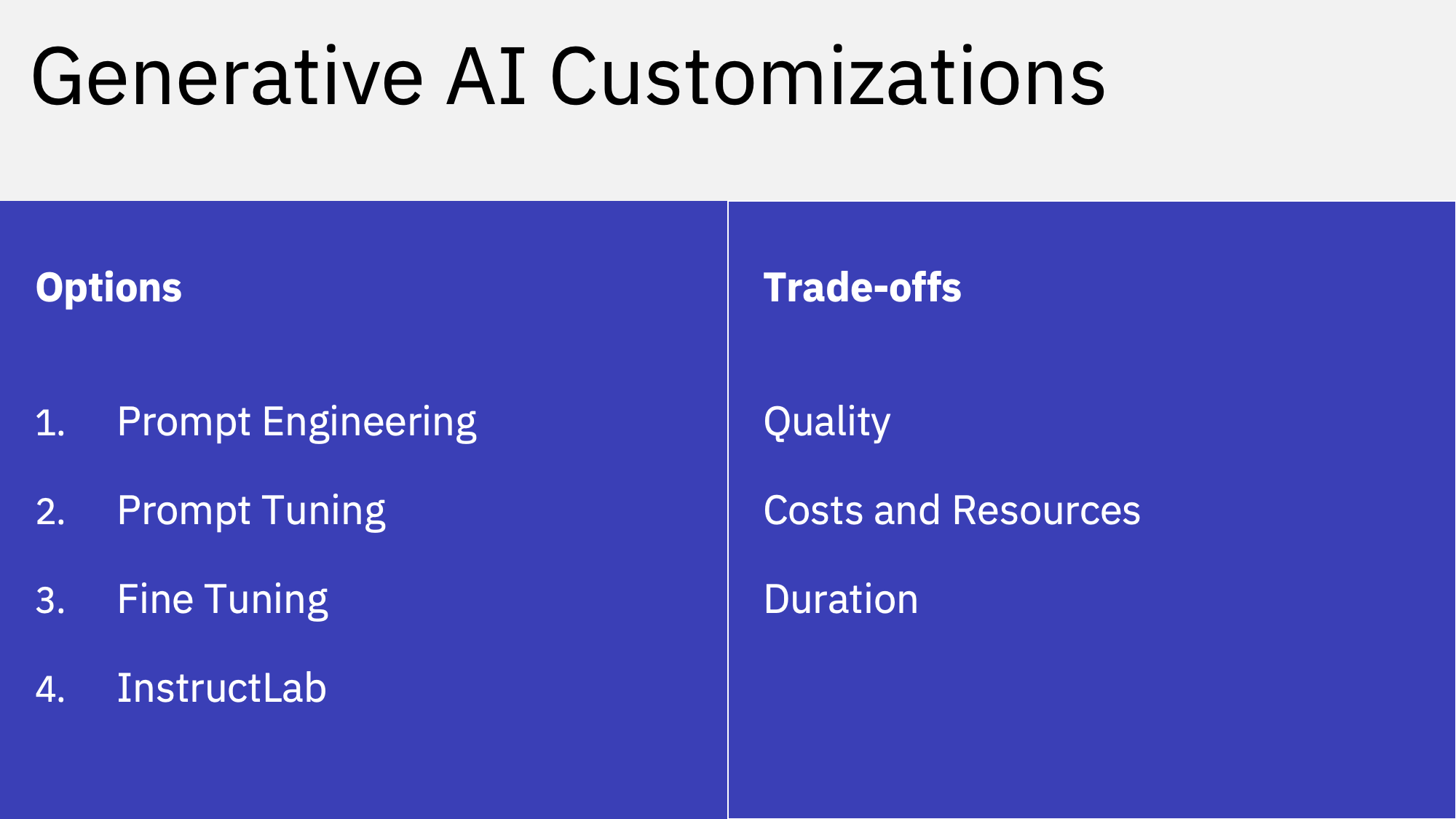
However, these pre-trained Large Language Models do not have to be re-trained for every AI tasks, since they contain a lot of general purpose knowledge already. There are different customization options with certain trade-offs.
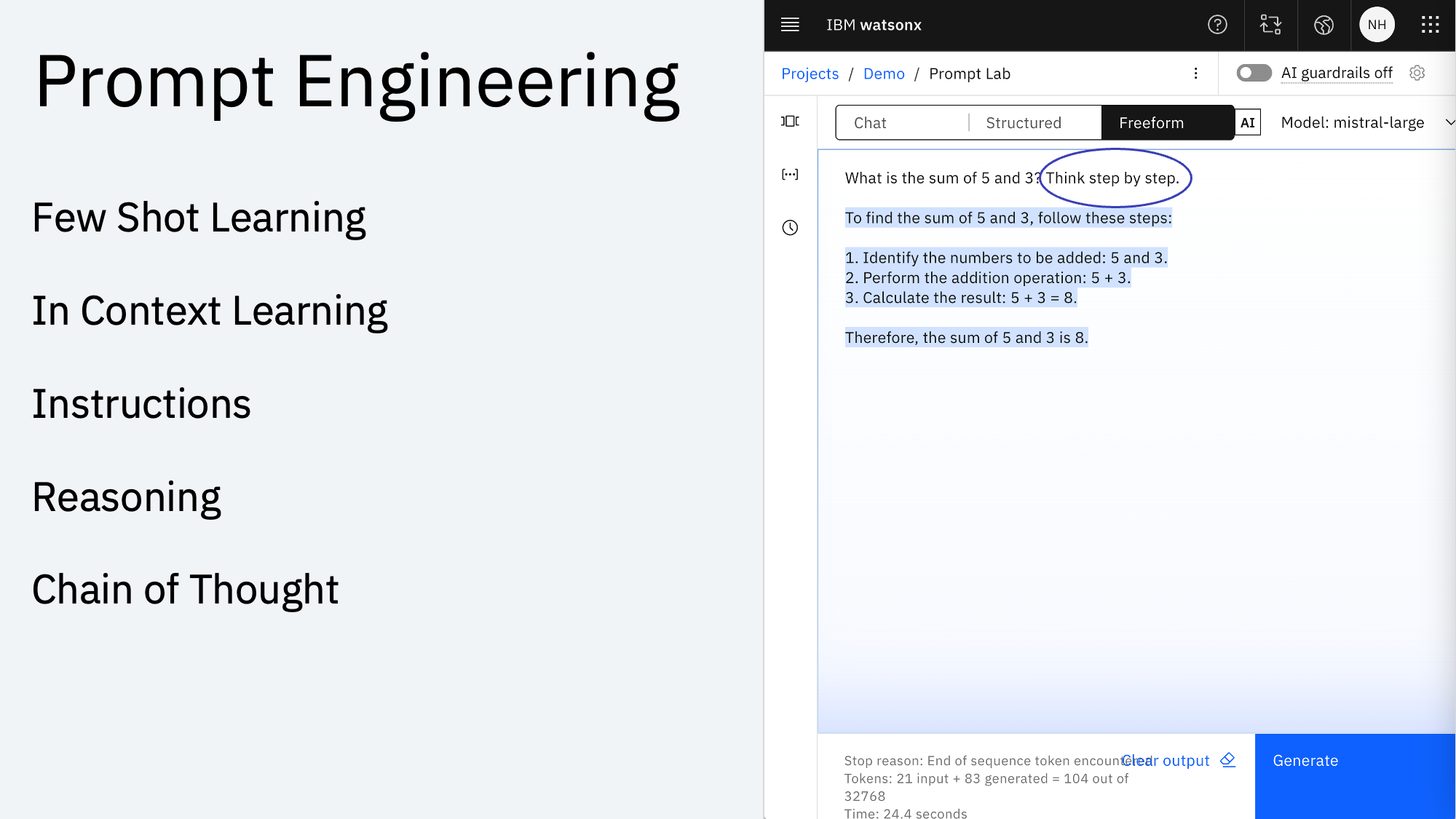
Prompt Engineering is a cheap way to instruct LLMs to generate the desired output. Techniques like Reasoning support the models to ‘think’ before they answer.
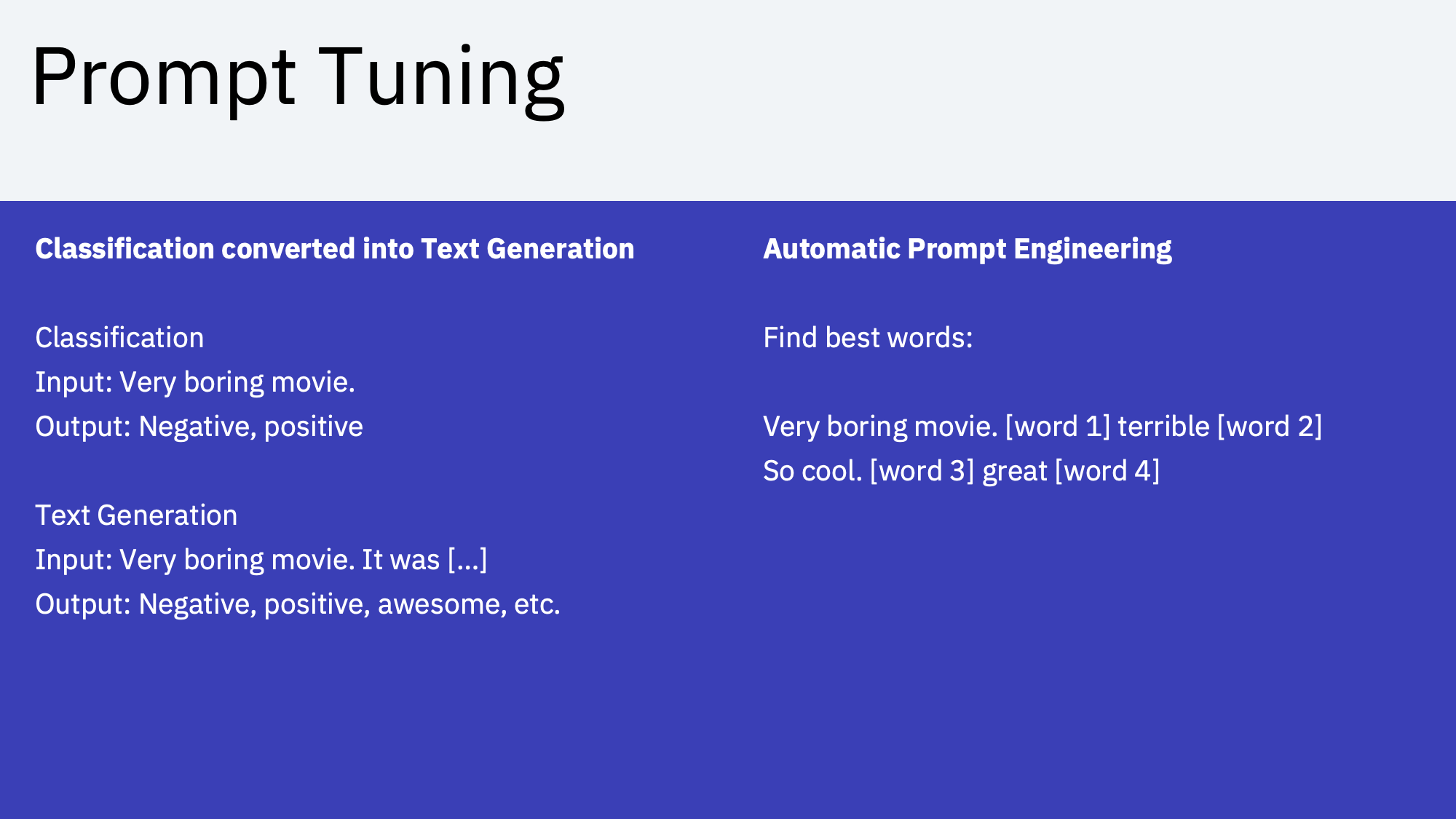
While Generative AI models usually ‘only’ predict the next words, different AI tasks can be converted into text generation tasks.
Prompt Tuning finds the best prompts automatically without having to change the model weights/parameters.
While Prompt Engineering and Prompt Tuning work well for certain scenarios, there are limitations in terms of quality of the generated output. Sometimes more labeled samples are needed that do not fit into a prompt for a model (context window).
With full Fine-tuning many more samples can be provided. Full Fine-tuning leverages the pre-trained models and changes all model weights, which makes this technique for many scenarios too expensive.
Recent innovations like LoRA and QLoRA address this issue, by changing only a small portion of the model parameters.
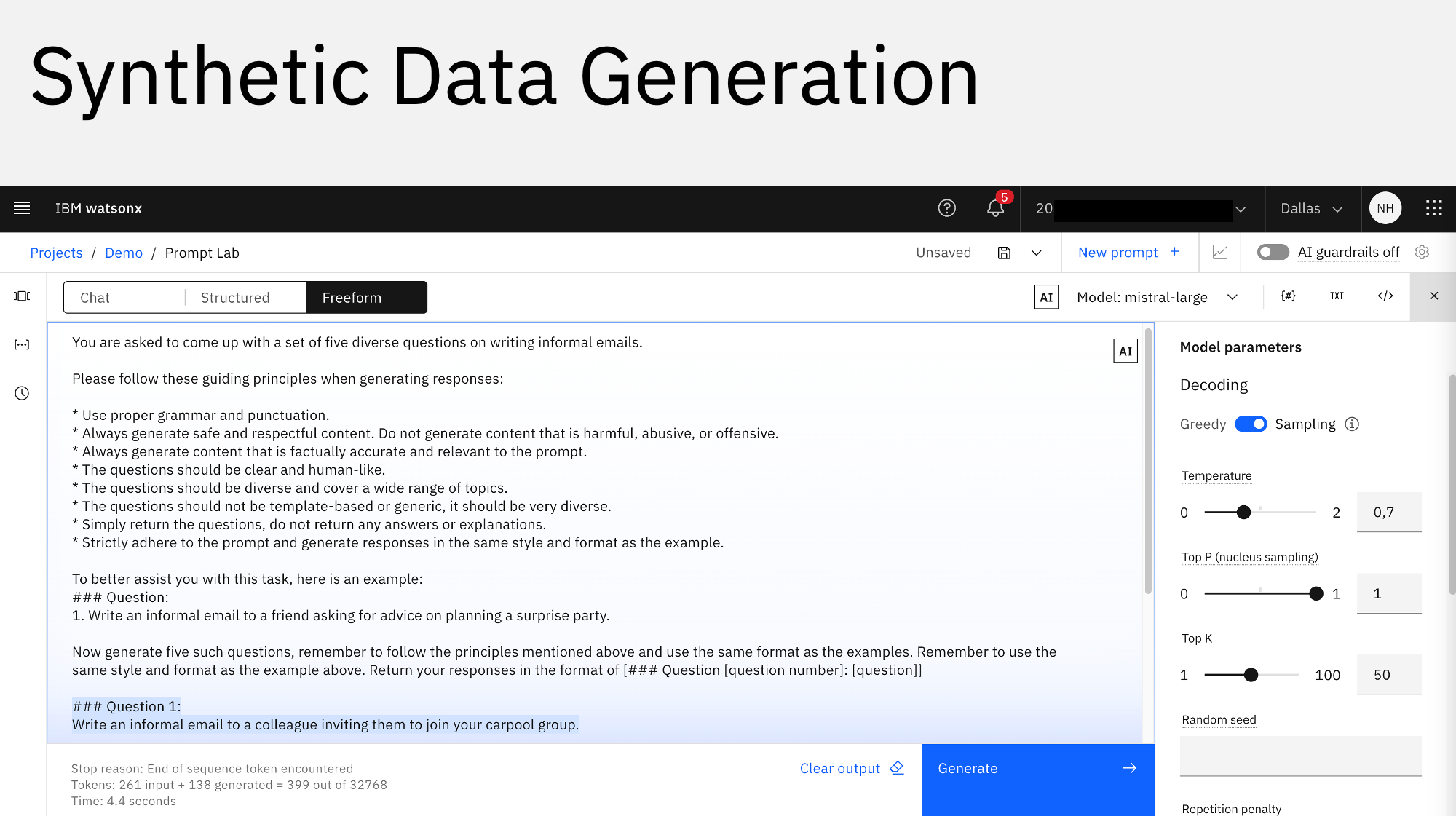
Fine-tuning of Generative AI models requires labeled data too, but not as much as classic Machine Learning models. Often synthetic data is generated which is cheaper and faster to get.
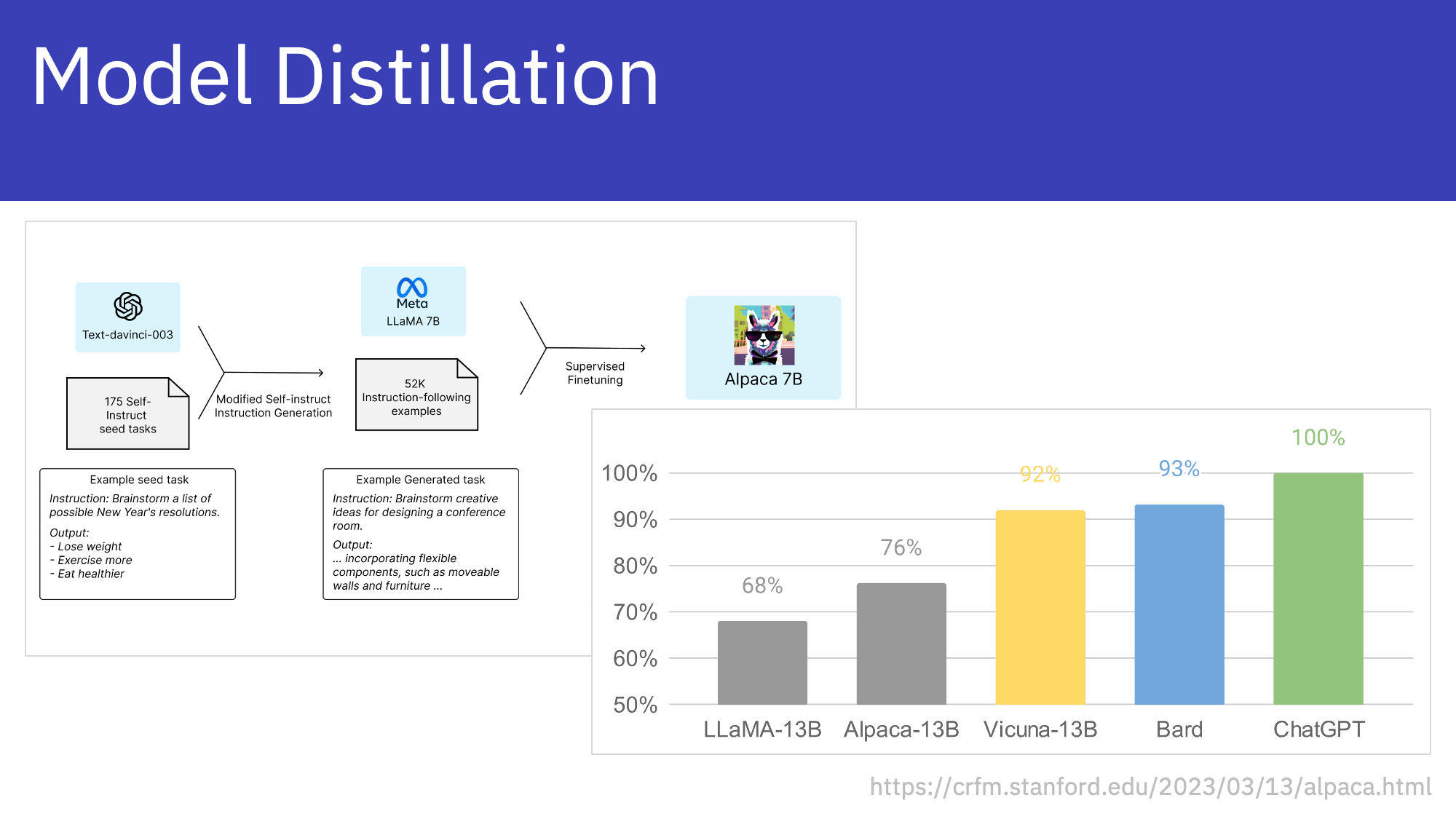
In March 2023 the Stanford University demonstrated how to use large Large Language Models to fine-tune smaller Large Language Models. The larger models generate data to fine-tune smaller models. Smaller fine-tuned models can provide better qualities than large models, are cheaper to operate and they have faster response times.
InstructLab
Introducing InstructLab. Let’s look at the definition from the landing page:
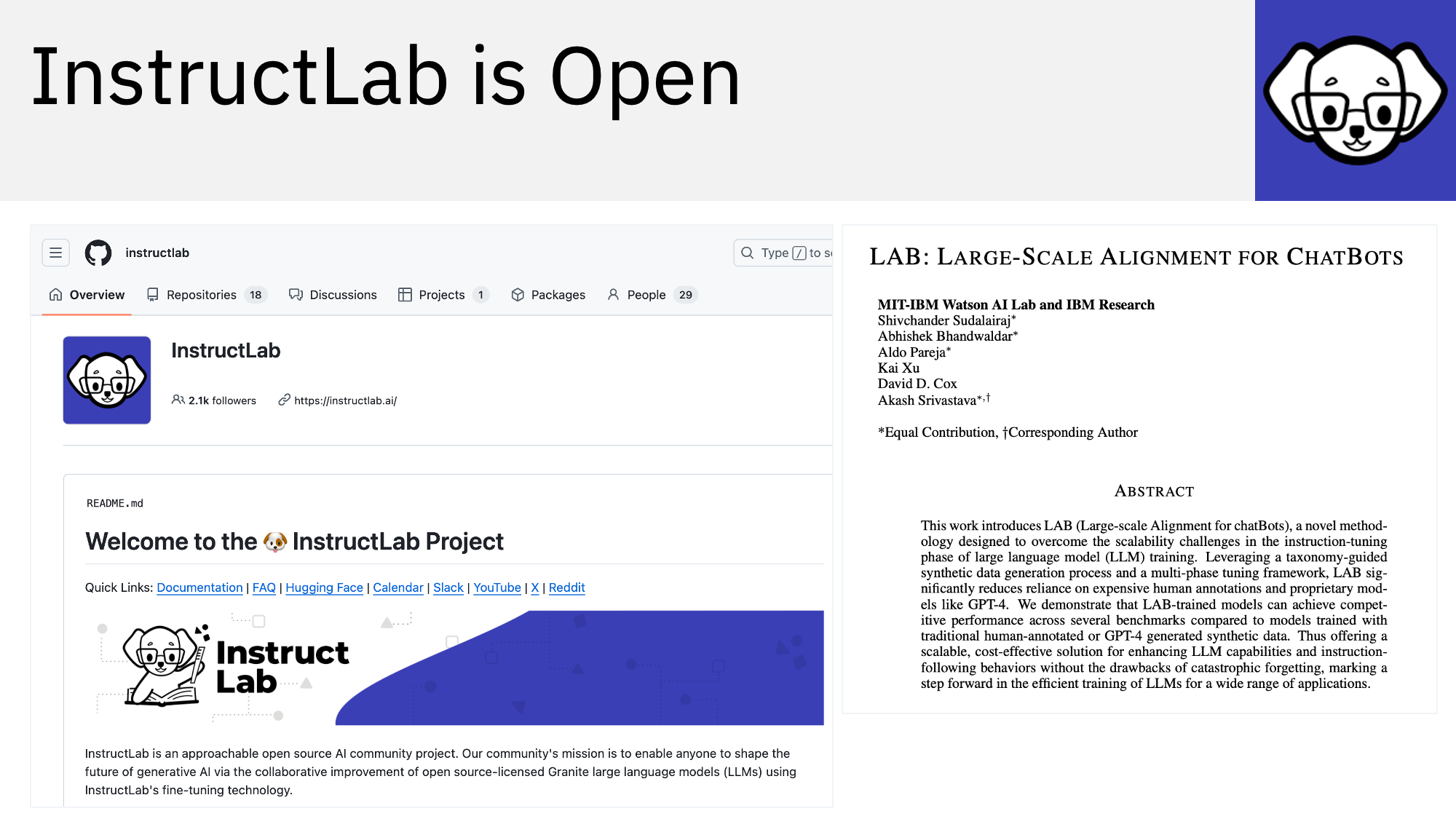
InstructLab is an approachable open source AI community project. Our community’s mission is to enable anyone to shape the future of generative AI via the collaborative improvement of open source-licensed Granite large language models (LLMs) using InstructLab’s fine-tuning technology. […] InstructLab allows anyone to improve an existing LLM by fine-tuning it with additional data sources. This allows LLMs to continuously gain new knowledge, supplementing gaps in their initial training, even about current events that happened since their pre-training phase.
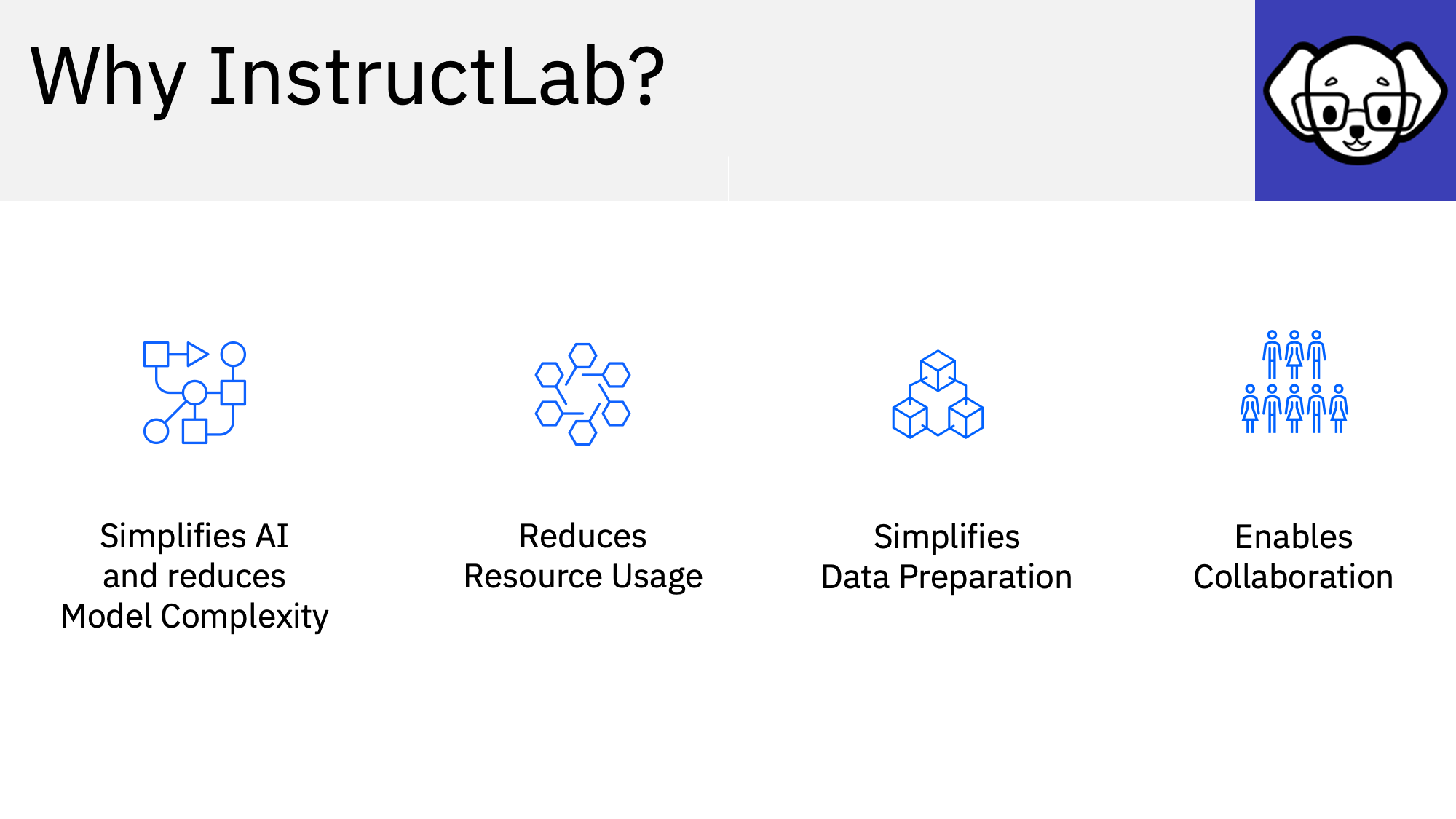
InstructLab combines several of the concepts mentioned above. To allow customizations with only a few data samples, synthetic data is generated in multiple steps. When generating data, it’s important to run evaluations to only pick high quality data. The smaller student models learn from the bigger teacher models.
InstructLab can be used without data science skills. For example, developers can utilize YAML files and technologies like llama.cpp, Apple silicon and Ollama to fine-tune and run models locally.
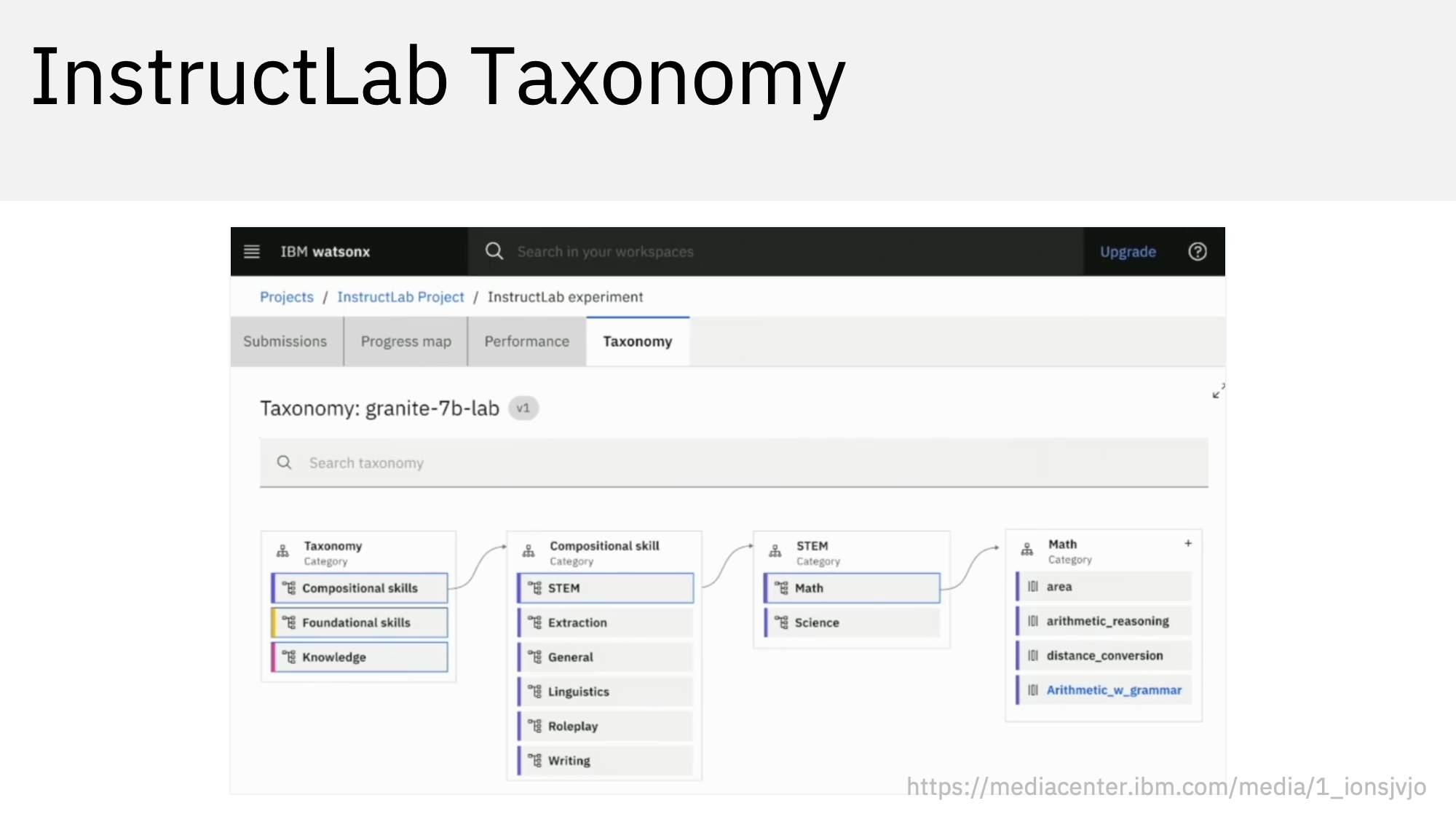
The paper Large-Scale Alignment for ChatBots describes the main concepts of InstructLab like taxonomies. Models can be fine-tuned for multiple AI tasks at the same time. Taxonomies help balancing knowledge and skills data and reduce the AI issue ‘Catastrophic Forgetting’.
InstructLab is available as open source. Give it a try!
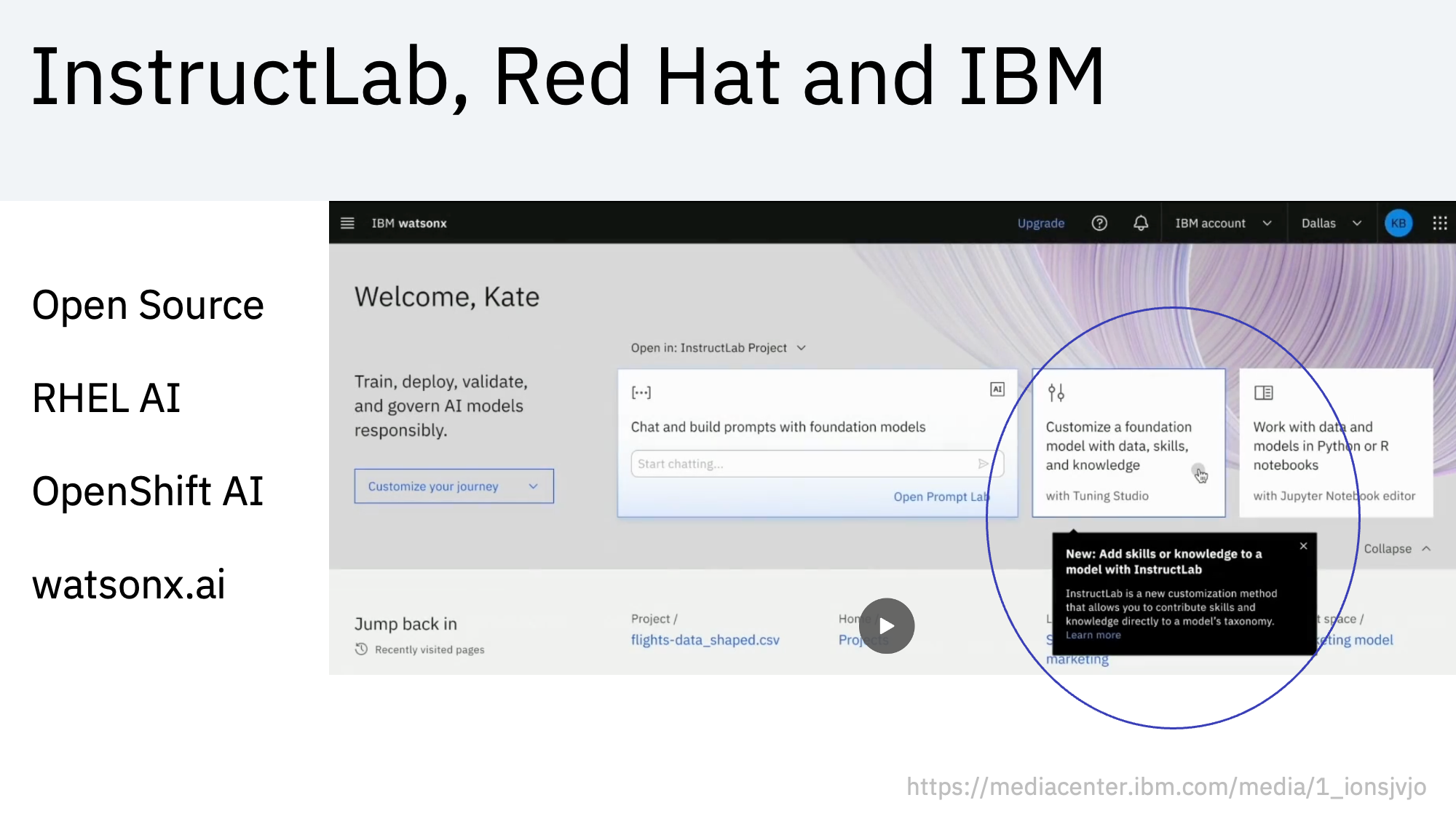
Red Hat offers Red Hat Enterprise Linux AI and Red Hat OpenShift AI which include InstructLab. IBM watsonx.ai extends OpenShift AI and contains additional functionality to build and manage AI applications. At the recent IBM TechXchange conference IBM announced support for InstructLab in watsonx.ai with supplemental features like data pipelines.
Next Steps
To learn more, check out the following resources: