Last week I described how to use Swagger in Spring Boot applications to document APIs. Below is a quick overview how to do this in Node.js applications.
As I wrote earlier I like the model to document APIs directly in the source code where the APIs are implemented. This helps developers to always remember to keep the implementation and the documentation of APIs in synch and it creates awareness for upwards compatibility of APIs. You can use this approach not only for Java applications but also for Node.js applications using the popular web application framework Express, for example via the npm module swagger-node-express. Check out the “findById” method in the sample.
However I’m not sure about the status of this module. It links to a GitHub project github.com/swagger-api/swagger-node-express that doesn’t seem to exist anymore. Instead it redirects to another library swagger-node which seems to be a successor or replacement. While the swagger-node library comes with a lot of additional nice capabilities I haven’t found out yet how to document the APIs directly in the source code. The swagger-node module uses separate yaml files to define the APIs. In this model the API documentation is close to the API implementation but not directly in the same files. Since the swagger-node module is linked from the Swagger site and since the code is in the swagger-api GitHub organization I describe below how to use this module in Node.js applications.
The library swagger-node comes with a nice editor to define APIs and an integrated web application to test APIs. Following an API first development process you can use a mock mode to “test” APIs without actually implementing the APIs/controllers. Via a verify command you can check whether the API definitions and project structures are correct. There is a wizard to create projects for different API frameworks like Express, Connect and others which creates the base structure and configuration for new projects.
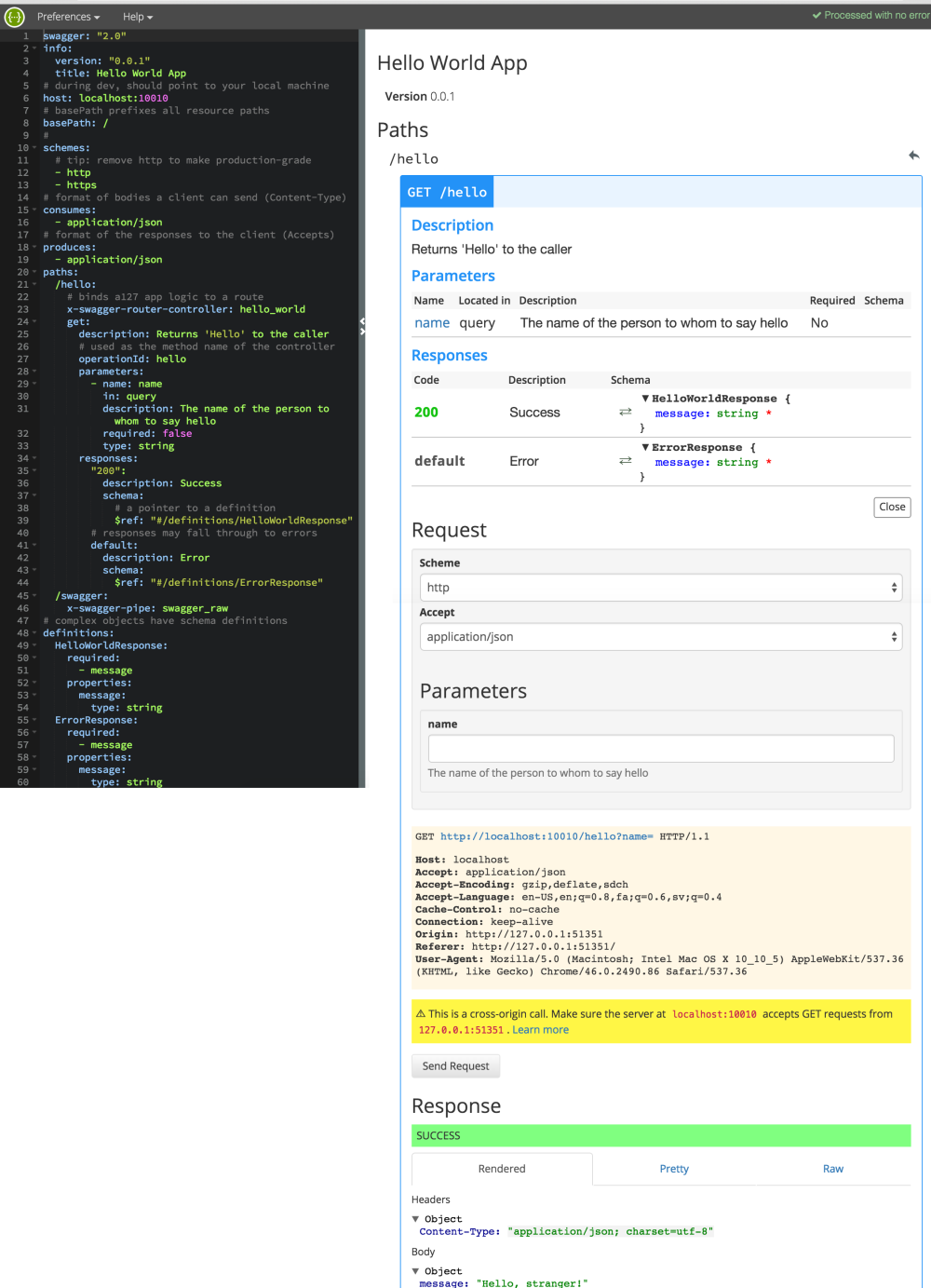
There is an easy to follow five steps instruction to build your first hello world sample. I won’t repeat the steps here. Just one thing that confused me. The sample defines that it returns JSON but actually it only returns a JSON content type with a string. So I changed one line in the file controllers/hello_world.js.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
function hello(req, res) {
// variables defined in the Swagger document can be referenced using req.swagger.params.{parameter_name}
var name = req.swagger.params.name.value || 'stranger';
var hello = util.format('Hello, %s!', name);
// this sends back a JSON response which is a single string
//res.json(hello);
res.json({ message: hello});
}
In order to start the Swagger project you need to invoke the command “swagger project start” or “node app.js” if you want to only run the core Node application. After this you can run the API and get the Swagger API definition.
http://127.0.0.1:10010/hello?name=Scott
http://127.0.0.1:10010/swagger
In order to run the editor invoke the command “swagger project edit”.
http://127.0.0.1:51351/#/
http://127.0.0.1:51351/editor/spec
Here is a screenshot of the editor with the hello world sample.