When fine-tuning large language models there is often not enough data available. This post describes how to use the Falcon model to generate synthetic data.
An incredible feature of Large Language Models is the ability to generate text, for example synthetic data that is similar to existing data. To do this, there are five prerequisites:
- The models need to be large enough and/or fine-tuned for specific tasks. Falcon 40b and the Falcon instruct version are great open source models.
- The model needs to have a larger input window.
- The license terms need to allow creating synthetical data to train other models.
- The instructions need to be good enough to generate similar data.
- There needs to be good examples and enough examples.
This is the prompt that Stanford univerity used to create 52k instructions for the manually created 175 instructions.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
You are asked to come up with a set of 20 diverse task instructions. These task instructions will be given to a GPT model and we will evaluate the GPT model for completing the instructions.
Here are the requirements:
1. Try not to repeat the verb for each instruction to maximize diversity.
2. The language used for the instruction also should be diverse. For example, you should combine questions with imperative instrucitons.
3. The type of instructions should be diverse. The list should include diverse types of tasks like open-ended generation, classification, editing, etc.
2. A GPT language model should be able to complete the instruction. For example, do not ask the assistant to create any visual or audio output. For another example, do not ask the assistant to wake you up at 5pm or set a reminder because it cannot perform any action.
3. The instructions should be in English.
4. The instructions should be 1 to 2 sentences long. Either an imperative sentence or a question is permitted.
5. You should generate an appropriate input to the instruction. The input field should contain a specific example provided for the instruction. It should involve realistic data and should not contain simple placeholders. The input should provide substantial content to make the instruction challenging but should ideally not exceed 100 words.
6. Not all instructions require input. For example, when a instruction asks about some general information, "what is the highest peak in the world", it is not necssary to provide a specific context. In this case, we simply put "<noinput>" in the input field.
7. The output should be an appropriate response to the instruction and the input. Make sure the output is less than 100 words.
List of 20 tasks:
Example
Let’s look at a very simple sample. The goal is to generate input data for retrieval-based Question Answering scenarios. Based on some documents, models need to find answers for given questions.
Here is how the prompt structure could look like. The full prompt with four sample documents is below.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Given the next [document], create a [question] and [answer] pair that are grounded
in the main point of the document, don't add any additional information that is
not in the document. The [question] is by an information-seeking User and the
[answer] is provided by a helping AI Agent.
[document]: IBM Closes Landmark Acquisition of Red Hat
IBM (NYSE:IBM) and Red Hat announced today that they have closed the transaction
under which IBM acquired all ...
[question]: How much did IBM pay for Red Hat?
[answer]: IBM acquired Red Hat for $190.00 per share in cash, representing a total
equity value of approximately $34 billion.
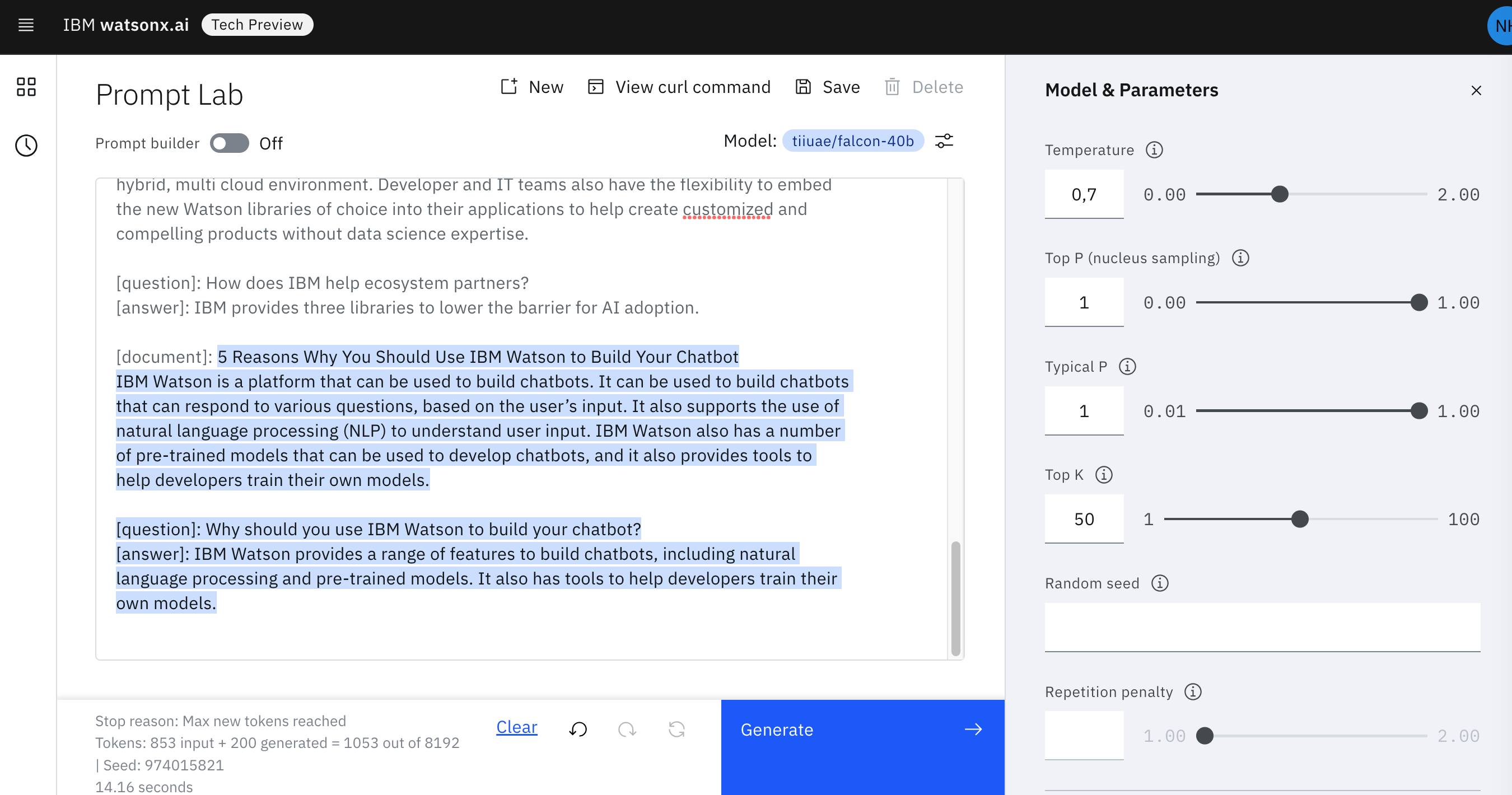
I’ve used Falcon 40b in Watsonx.ai with sampling and a temperature of 0.7. The output is amazing. Falcon came up with a document about IBM Watson, a good answer and a content grounded answer. It picked content about IBM Watson since the four sample documents contain IBM and Watson.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
[document]: 5 Reasons Why You Should Use IBM Watson to Build Your Chatbot
IBM Watson is a platform that can be used to build chatbots. It can be used to
build chatbots that can respond to various questions, based on the user’s input.
It also supports the use of natural language processing (NLP) to understand user
input. IBM Watson also has a number of pre-trained models that can be used to
develop chatbots, and it also provides tools to help developers train their own
models.
[question]: Why should you use IBM Watson to build your chatbot?
[answer]: IBM Watson provides a range of features to build chatbots, including
natural language processing and pre-trained models. It also has tools to help
developers train their own models.
In the next step you typically validate the generated output. For example, there should be some checks whether the answer addresses the question and whether the answer is grounded on the document. To do this, large language models can help that check for similarities and overlaps.
Full Prompt
Here is the full prompt if you want to try it yourselves:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
Given the next [document], create a [question] and [answer] pair that are grounded in the main point of the document, don't add any additional information that is not in the document. The [question] is by an information-seeking user and the [answer] is provided by a helping AI Agent.
[document]: IBM Closes Landmark Acquisition of Red Hat; Defines Open, Hybrid Cloud Future
IBM (NYSE:IBM) and Red Hat announced today that they have closed the transaction under which IBM acquired all of the issued and outstanding common shares of Red Hat for $190.00 per share in cash, representing a total equity value of approximately $34 billion. The acquisition redefines the cloud market for business. Red Hat’s open hybrid cloud technologies are now paired with the unmatched scale and depth of IBM’s innovation and industry expertise, and sales leadership in more than 175 countries. Together, IBM and Red Hat will accelerate innovation by offering a next-generation hybrid multicloud platform. Based on open source technologies, such as Linux and Kubernetes, the platform will allow businesses to securely deploy, run and manage data and applications on-premises and on private and multiple public clouds.
[question]: How much did IBM pay for Red Hat?
[answer]: IBM acquired Red Hat for $190.00 per share in cash, representing a total equity value of approximately $34 billion.
[document]: IBM acquires Red Hat: It's official - IBM has acquired Red Hat! The deal was announced in October 2018. IBM Closes Landmark Acquisition of Red Hat.
[question]: When did IBM acquire Red Hat?
[answer]: IBM acquired Red Hat in 2018.
[document]: Running and Deploying IBM Watson NLP Containers
IBM Watson NLP (Natural Language Understanding) and Watson Speech containers can be run locally, on-premises or Kubernetes and OpenShift clusters. Via REST and gRCP APIs AI can easily be embedded in applications. This post describes different options how to run and deploy Watson NLP. To set some context, check out the landing page IBM Watson NLP Library for Embed. The Watson NLP containers can be run on different container platforms, they provide REST and gRCP interfaces, they can be extended with custom models and they can easily be embedded in solutions. While this offering is new, the underlaying functionality has been used and optimized for a long time in IBM offerings like the IBM Watson Assistant and NLU (Natural Language Understanding) SaaS services and IBM Cloud Pak for Data. Via kubectl or oc Kubernetes resources can be deployed. The Watson NLP pod contains the NLP runtime container and potentially multiple init containers. Each init container contains either predefined or custom models.
[question]: Which interfaces does Watson NLP provide?
[answer]: The Watson NLP containers support REST and gRPC.
[document]: IBM Helps Ecosystem Partners Accelerate AI Adoption by Making it Easier to Embed and Scale AI Across Their Business
IBM (NYSE: IBM) today announced an expansion to its embeddable AI software portfolio with the release of three new libraries designed to help IBM Ecosystem partners, clients and developers more easily, quickly and cost-effectively build their own AI-powered solutions and bring them to market. The expanded portfolio provides access to the same AI libraries that power popular IBM Watson products. It is designed to help lower the barrier for AI adoption by helping partners and clients address the skills shortage and development costs required to build machine learning and AI models from scratch. Generally available today, the AI libraries were developed in IBM Research and designed to provide Independent Software Vendors (ISVs) across industries an easily scalable way to build natural language processing, speech to text, and text to speech capabilities into applications across any hybrid, multi cloud environment. Developer and IT teams also have the flexibility to embed the new Watson libraries of choice into their applications to help create customized and compelling products without data science expertise.
[question]: How does IBM help ecosystem partners?
[answer]: IBM provides three libraries to lower the barrier for AI adoption.
[document]:
Next Steps
To learn more, check out the Watsonx.ai documentation and the Watsonx.ai landing page.