This article describes how to deploy and configure the GitOps tool ArgoCD on OpenShift.
GitOps Operator
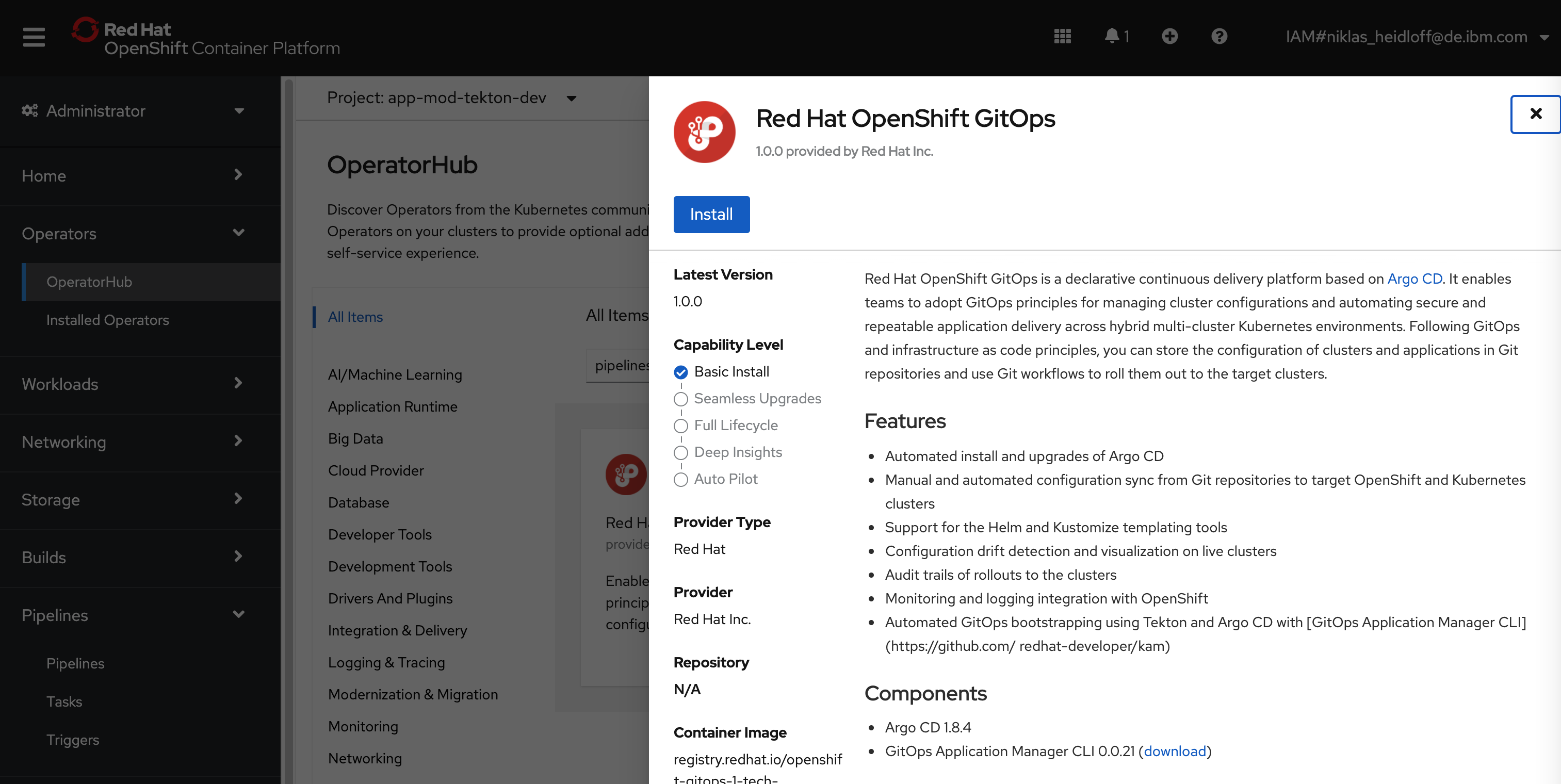
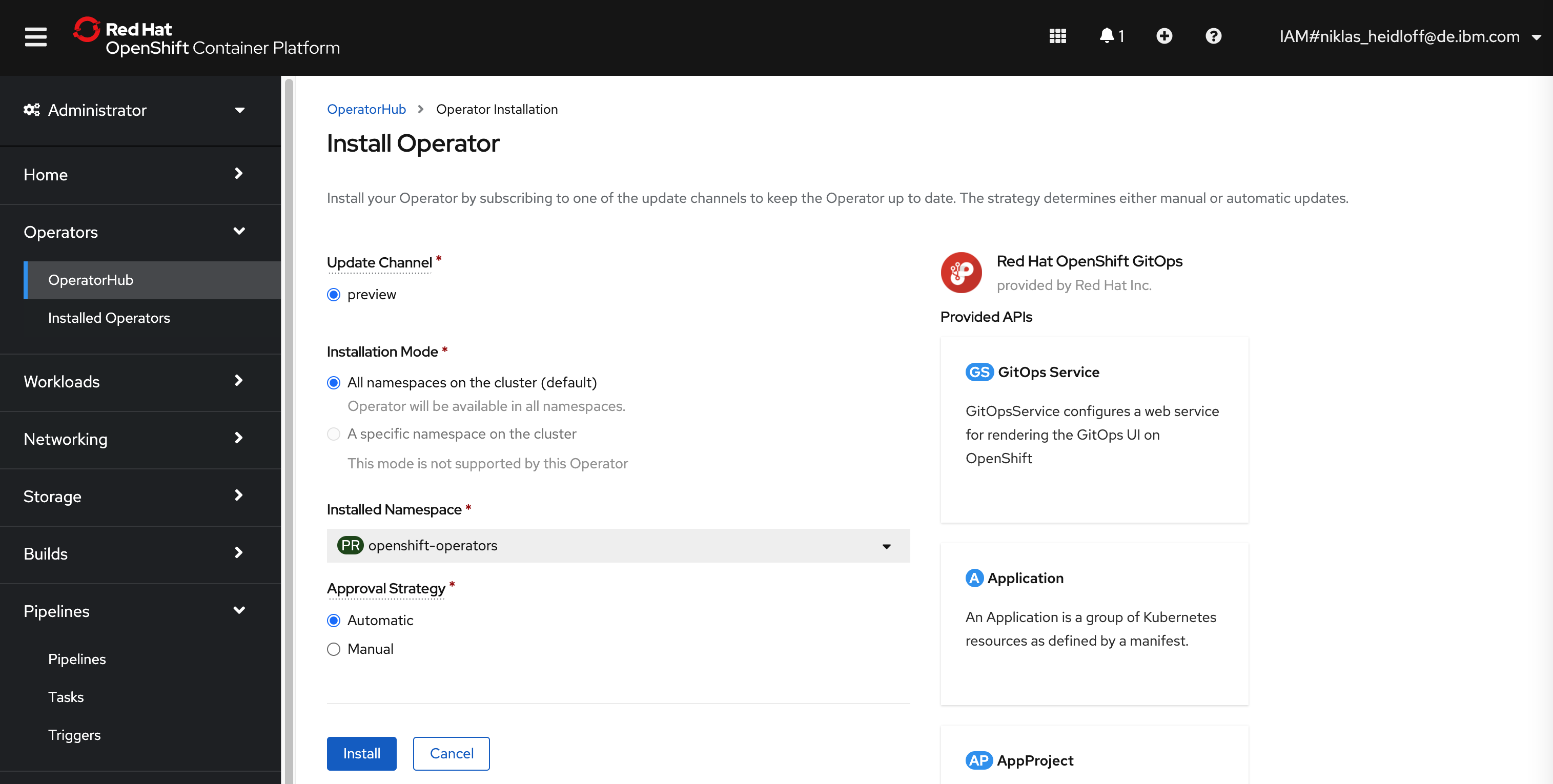
In order to install GitOps in OpenShift, there is an operator ‘Red Hat OpenShift GitOps’. The installation is trivial. You can use the default values.
ArgoCD Console
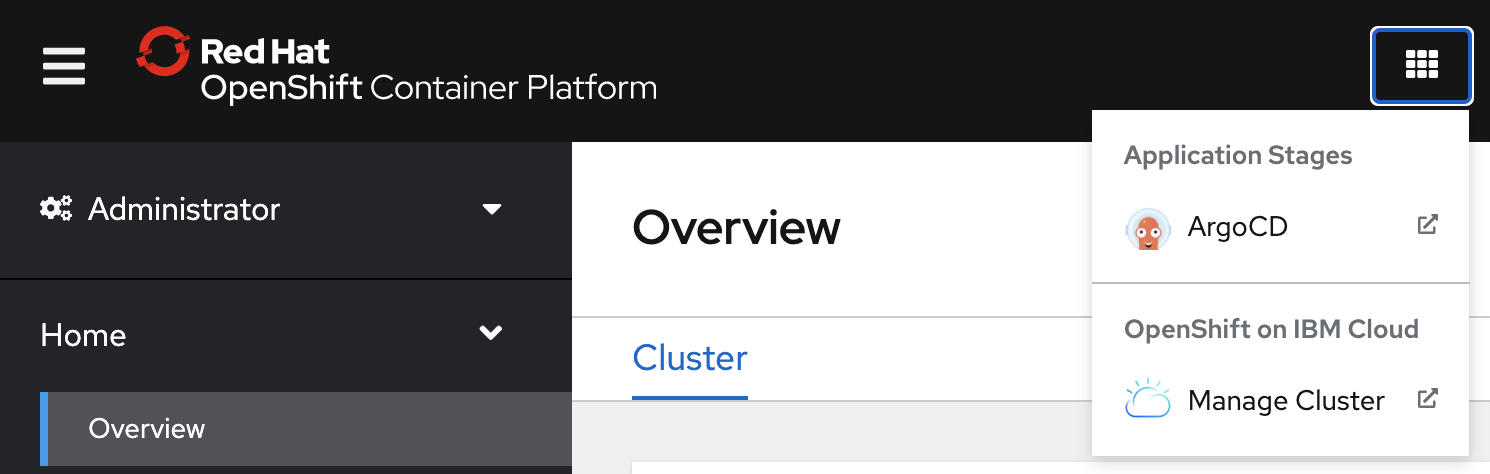
In many cases the first thing you want to do is to launch the ArgoCD console. This can be done from the following menu.
The golden question is what the username and password is. Invoke these commands to find out:
$ oc get route argocd-cluster-server -n openshift-gitops --template='{{ .spec.host }}'
$ kubectl -n openshift-gitops get secret argocd-cluster-cluster -o 'go-template={{index .data "admin.password"}}' | base64 -d
$ echo user: adminArgoCD Configuration Prerequisites
Installing ArgoCD is easy. However the configuration is a little more tricky. The most important things you need are …
- ArgoCD token
- GitHub ssh private key
- GitHub URL of GitOps repo
In my application modernization project I use Tekton and ArgoCD to deploy the application. In order to check these prerequisites, I have implemented a script.
In order to access GitHub projects on behalf of users, you need to set up keys. See my article Accessing GitHub in Tekton Tasks on OpenShift for details.
For the communication between ArgoCD, Tekton and OpenShift an ArgoCD token is necessary. In your ArgoCD console open ‘/settings/accounts/tekton’, generate a new token and copy it to the clipboard.
ArgoCD Configuration
Once you have all necessary information the actual configuration needs to be done. I have written a script that does all of this for a common setup. Let’s take a look at some of the key steps.
I’m using four projects: Pipelines, dev, test, production.
1
2
3
4
oc project app-mod-argocd-pipelines > /dev/null 2>&1
if [ $? != 0 ]; then
oc new-project app-mod-argocd-pipelines
fi
The ArgoCD token and the GitHub ssh private key need to be stored in secrets:
1
2
oc create secret -n app-mod-argocd-pipelines generic argocd-env-secret '--from-literal=ARGOCD_AUTH_TOKEN=${TOKEN_ARGOCD}'
oc apply -f ${ROOT_FOLDER}/scripts-openshift-argocd/argocd-config/tekton-git-ssh-secret.yaml
In order to allow pipelines to access other projects, a service account is used with the appropriate access.
1
2
oc apply -f ${ROOT_FOLDER}/scripts-openshift-argocd/argocd-config/service-account.yaml
oc policy add-role-to-user edit system:serviceaccount:app-mod-argocd-pipelines:pipeline -n app-mod-argocd-dev
In order to share status information between the different projects, a cluster role is used with the appropriate access.
1
2
3
4
oc apply -f ${ROOT_FOLDER}/scripts-openshift-tekton/ClusterRole.yaml
oc create clusterrolebinding routes-and-services-reader \
--clusterrole=routes-and-services-reader \
--serviceaccount=app-mod-argocd-pipelines:pipeline
In order to synchronize between the ‘to be state’ in the GitOps repo and the ‘is state’ in Kubernetes, ArgoCD is used. For each OpenShift project / Kubernetes namespace one ArgoCD project is defined.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: app-dev
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
destination:
namespace: app-mod-argocd-dev
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: default
source:
path: service-catalog-quarkus-reactive/dev
repoURL: https://github.com/<your-github-name>/application-modernization-javaee-quarkus-config.git
targetRevision: main
syncPolicy: {}
In the ArgoCD project template files the GitHub URLs are corrected:
1
2
3
GITHUB_NAME=$(echo "$GITHUB_CONFIG_URL" | cut -d'/' -f 4)
sed "s/<your-github-name>/${GITHUB_NAME}/g" ${ROOT_FOLDER}/scripts-openshift-argocd/argocd-config/argocd-app-dev.yaml.template > ${ROOT_FOLDER}/scripts-openshift-argocd/argocd-config/argocd-app-dev.yaml
oc apply -f ${ROOT_FOLDER}/scripts-openshift-argocd/argocd-config/argocd-app-dev.yaml
Next Steps
To learn more about Tekton, ArgoCD and application modernization, check out my repo.