Apache Spark comes with a set of machine learning samples. One of those sample is a movie recommendation system which makes personalized recommendations based on a technique called Collaborative Filtering. In this article I describe on a high level how this sample works.
For more details check out the tutorial from the Berkeley university. The dataset used in that tutorial contains 10 million ratings from 72,000 users on 10,000 movies. The Spark project comes with a synthetic dataset in the same format which I’ve used below.
In the first step the data is read from a file into an RDD. Each row contains one rating in the format “UserId::MovieId::Rating” where the rating is between 1 and 5.
1
2
3
4
val ratings = sc.textFile("sample_movielens_ratings.txt").map { line =>
val fields = line.split("::")
Rating(fields(0).toInt, fields(1).toInt, fields(2).toDouble)
}
Next the data is split in two parts for the training and later testing. Another typical approach is to have a third dataset in order to validate the best model if you compared multiple models.
1
2
3
val splits = ratings.randomSplit(Array(0.8, 0.2))
val training = splits(0).cache()
val test = splits(1).cache()
The training is done via the Collaborative Filtering algorithm Alternating Least Squares (ALS). Essentially this technique predicts missing ratings for specific users for specific movies based on ratings for those movies from other users who did similar ratings for other movies. Read the documentation for more details.
Collaborative filtering is commonly used for recommender systems. These techniques aim to fill in the missing entries of a user-item association matrix. spark.mllib currently supports model-based collaborative filtering, in which users and products are described by a small set of latent factors that can be used to predict missing entries. spark.mllib uses the alternating least squares (ALS) algorithm to learn these latent factors.
In order to find the best model you should run the ALS algorithm with different parameters (see documentation). Honestly I don’t know yet what these parameters really do. My understanding is that you should simply try different values and compare the results.
The RDD ‘training’ needs to have a specific format with the user id, product (movie) id and rating. While this sample uses spark.mllib and RDDs there is a similar version of the same sample which uses spark.ml and dataframes. In that case you can pass the column names of user, movie and rating as parameters to the ALS function.
1
2
3
4
5
val model = new ALS()
.setRank(params.rank)
.setIterations(params.numIterations)
.setLambda(params.lambda)
.run(training)
In order to verify the quality of the models Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) is used to measure the differences between values predicted by a model and the values actually observed. The smaller the calculated error, the better the model. In order to test the quality of the model, the test data is used (which was split above).
1
2
var rmseTest = computeRmse(modelLowestRmse.get, test, true)
println(s"Test RMSE = $rmseTest.")
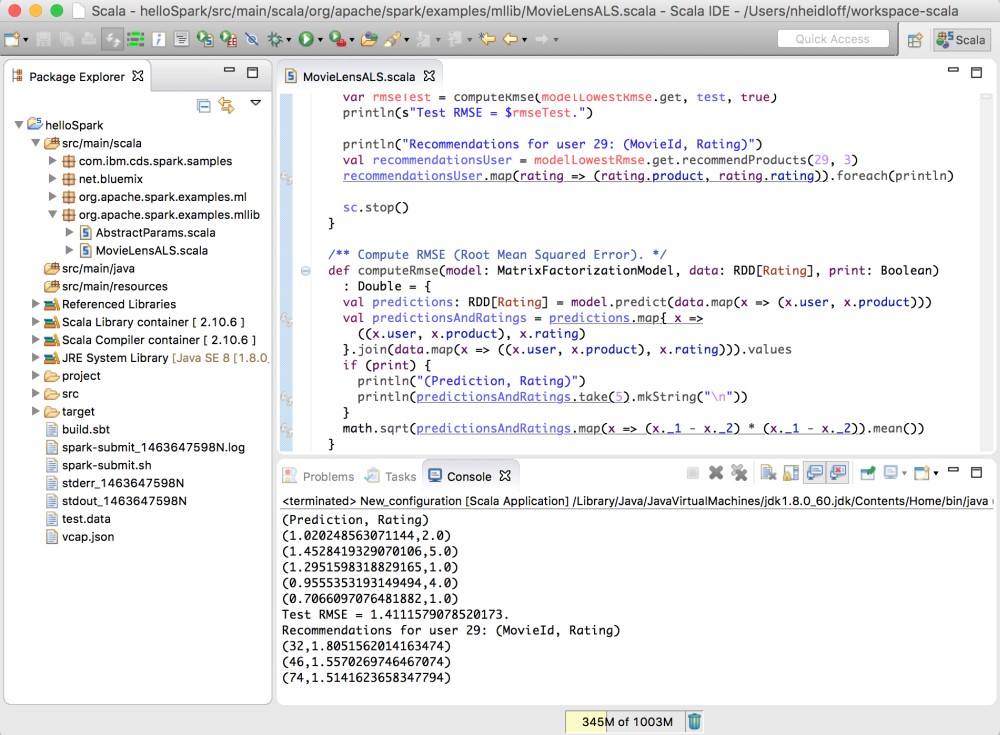
I’ve added some code to computeRmse to display some predictions and actual ratings.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
def computeRmse(model: MatrixFactorizationModel, data: RDD[Rating], print: Boolean)
: Double = {
val predictions: RDD[Rating] = model.predict(data.map(x => (x.user, x.product)))
val predictionsAndRatings = predictions.map{ x =>((x.user, x.product), x.rating)
}.join(data.map(x => ((x.user, x.product), x.rating))).values
if (print) {
println("(Prediction, Rating)")
println(predictionsAndRatings.take(5).mkString("\n"))
}
math.sqrt(predictionsAndRatings.map(x => (x._1 - x._2) * (x._1 - x._2)).mean())
}
After the best model has been found recommendations for specific users for specific movies can be made. Since the synthetic dataset doesn’t contain the movie information only movie ids are displayed.
1
2
3
println("Recommendations for user 29: (MovieId, Rating)")
val recommendationsUser = modelLowestRmse.get.recommendProducts(29, 3)
recommendationsUser.map(rating => (rating.product, rating.rating)).foreach(println)
The following screenshot shows the output of the code above. The results are actually not that good for the synthetic dataset but according to the Berkeley tutorial better for real data.
I’ve run the code in a Scala IDE. Check out my previous article to learn how to set the IDE up and how to deploy the code to Spark on Bluemix.